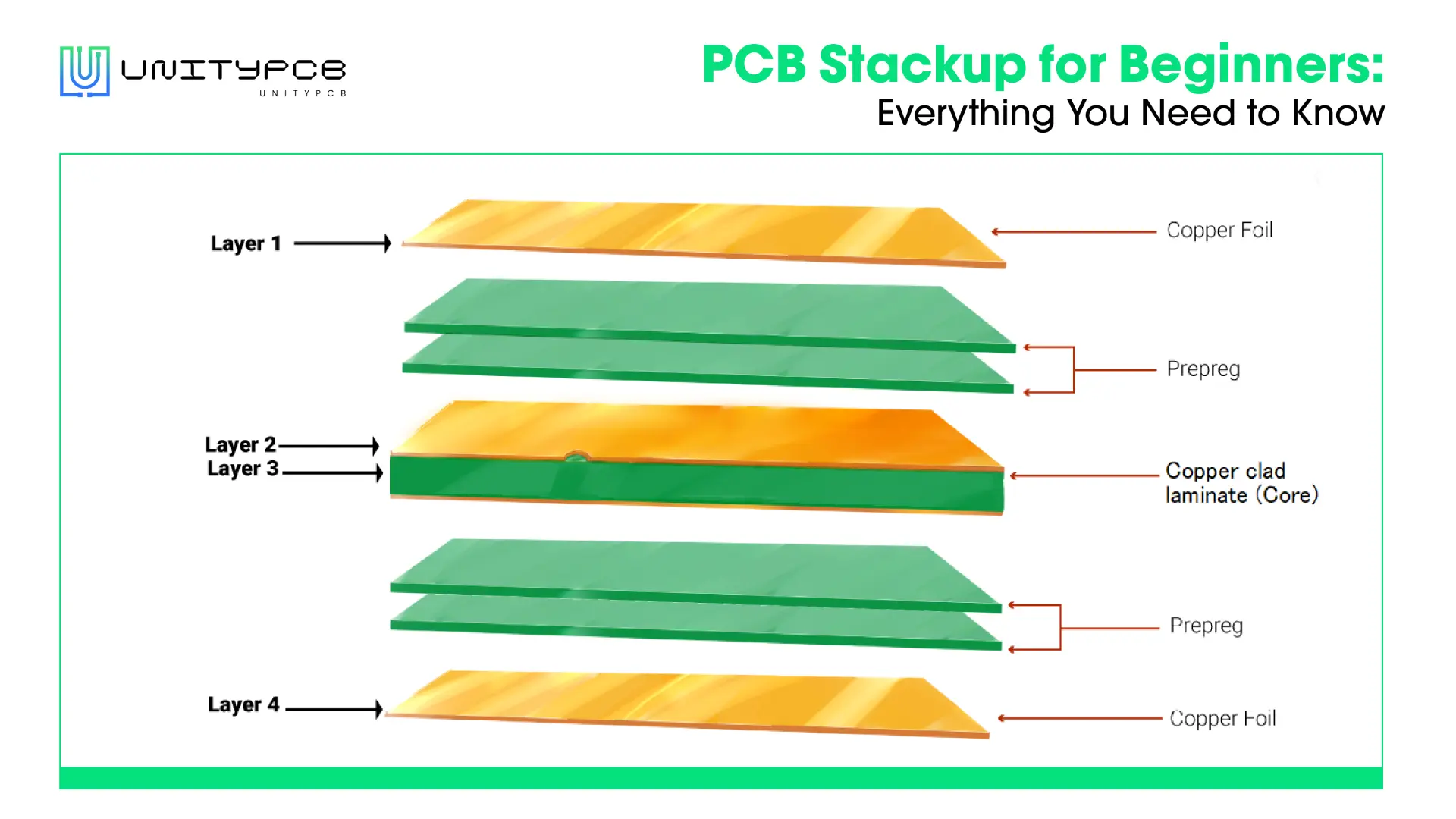
No matter what type of circuit board, it needs mechanical support, which is the PCB substrate. Substrate material selection is usually one of the first decisions we must make when designing a board. The material and properties of the PCB substrate will affect the performance of the final PCB. In this blog, we list the PCB substrate’s top 4 properties that need to be considered and 6 common substrate materials.
What Is a PCB Substrate?
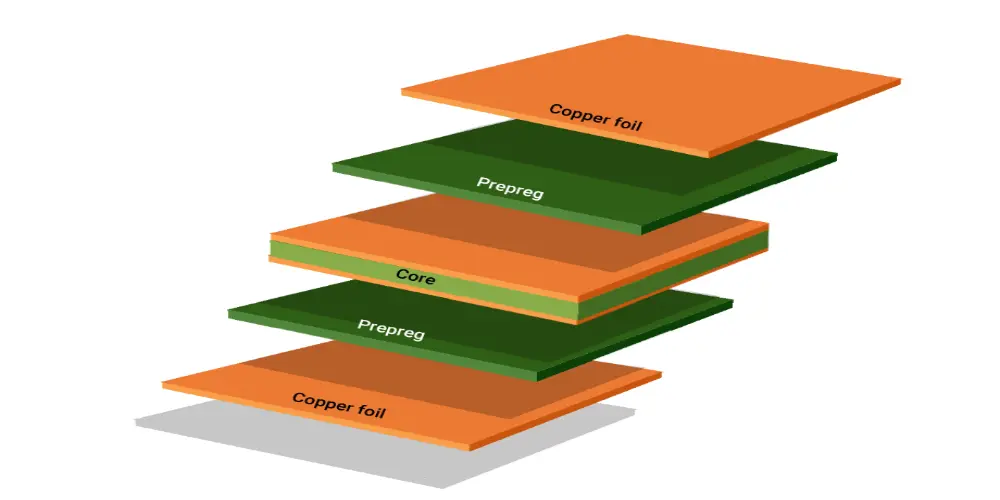
PCB substrate is the core support structure of a circuit board, providing mechanical support, electrical connection, and thermal management functions. Usually, a substrate is normally made of insulated material, laminating copper foils on it to generate a conductive path. The PCB substrate may be rigid or flexible depending on the material used. Its material and structure directly determine the performance of the board, including the strength, flexibility, and reliability of the circuit board. The electrical properties of the PCB substrate material (such as dielectric constant and loss tangent) also affect the transmission quality of high-frequency signals.
Top 4 Properties to Consider When Selecting PCB Substrates
Dielectric Constant (DK) and Dielectric Loss (DF)
The DK value indicates the signal’s integrity and quality as it passes through the material. The low values help reduce signal distortions and reflections, enabling good signal transmission at high speeds. The loss tangent defines the dissipation factor, that is, the power loss due to the material. The less the value, the less the loss.
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
It reflects what temperature that the material shifts from a hard to a soft state. The FR-4 material Tg is within the range of 130℃ to 140℃, and the high Tg material is above 170℃. The properties of high Tg materials during working conditions at high temperatures are much better in stability and reliability. When the circuit board’s operating temperature exceeds Tg, the substrate will probably lose its structural integrity and may be deformed or even fail. The appropriate Tg will be selected based on the needed assembly process. For lead-free assembly, the minimum recommended is 170℃.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
CTE is a measurement of a material’s rate of expansion under temperature changes. Materials with high CTE will expand more than materials with low CTE, which can cause internal stress and potential damage. In multilayer PCBs, if the substrates that make up the various layers have different CTE, the separation between layers may occur when the PCB is subjected to temperature changes.
The substrate materials should be selected to have a CTE as close to the components as possible, which can reduce thermal stress and prevent potential damage. The material with low CTE is considered an ideal choice for PCB substrate. With a lower expansion rate, it could reduce the deformations that may arise under temperature changes. That will make the PCB and its components work long-lasting.
Thermal Conductivity (K)
Materials with high thermal conductivity are able to dissipate the generated heat more effectively, and this is very critical in highly powered devices. The heat generated by high-power or sensitive components can be effectively transferred to a heat sink or ground plane. If the substrate’s thermal conductivity is too low, there is a danger of heat accumulation, leading to local high temperatures and component failure.
Common Types of Circuit Board Substrate Materials
In this section, we will introduce 6 types of PCB substrate materials, you can have a better understanding when go through below.
FR-4: The Most Widely Used Material
FR-4 is the most general substrate material in the PCB industry. It consists of a composite material of glass fiber and epoxy resin. FR-4 is renowned for its low cost, mechanical strength, and superior electrical insulation. Despite its excellent overall performance, this material is not suitable for high-speed or high-frequency applications due to its high dielectric loss. For PCB designs that pursue cost-effectiveness, FR-4 is undoubtedly the best choice.
Discover More: FR4 PCB: A Guide to FR4 Material in Circuit Boards
Polyimide: The Go-To Material for Flexible PCB Designs
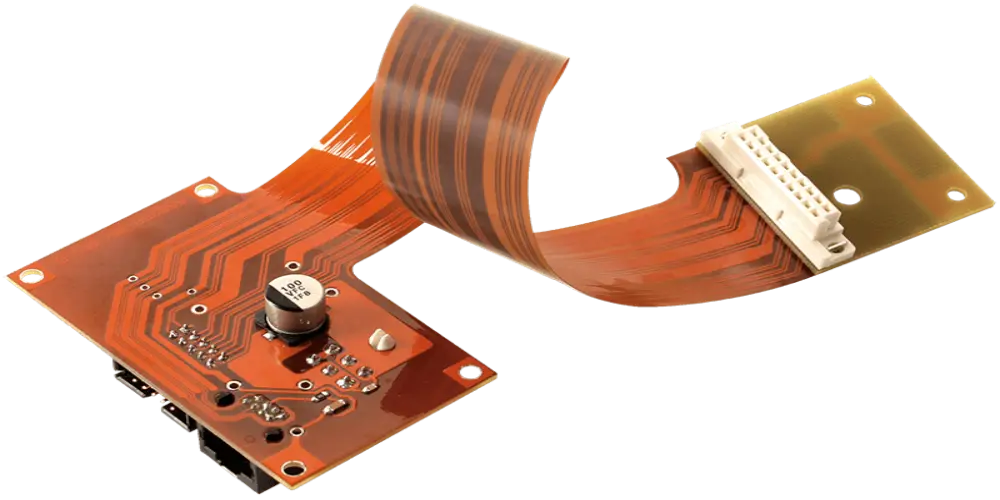
Polyimide is the preferred PCB substrate material for flexible circuit boards and works well in applications that call for bending or folding. This material has extremely high heat resistance (Tg above 250°C), excellent electrical insulation properties, and amazing flexibility. Compared with traditional FR-4, polyimide can work in extreme temperatures while maintaining material flexibility and reliability, but the cost is relatively high.
PTFE: The Preferred Substrate for High-Frequency Boards
PTFE is a special type of PCB substrate material that offers magnificent advantages in high-frequency and high-speed PCBs. Indeed, the DK and the DF of this material are extremely low. It can reliably support signals from hundreds of MHz to tens of GHz. It is thus often utilized in communications equipment, radar systems, and RF antennas. Its performance in demanding applications is further improved by its resistance to high temperatures and lightweight nature.
Rogers: Exceptional for High-Performance PCBs
Rogers is a member of the high-performance material class. It has a low CTE, excellent electrical properties, and high thermal conductivity. Besides, Rogers material excels in high-frequency, high-performance devices. Being developed by Rogers Corporation, this advanced material is now ideal for high-end electronic products owing to its stable quality and reliability.
Metal Core: Superior Thermal Management Solution
Metal core PCB (MCPCB) is a board with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the PCB substrate. It has significant thermal management advantages over traditional materials. This advanced PCB is especially suitable for high-heat applications such as high-power LED lighting, which can efficiently conduct and dissipate heat.
Ceramic: A Balanced Solution for Thermal and Electrical Performance
Ceramic substrates have superior excellent thermal and electrical characteristics. Ceramic materials with exceptionally high heat conductivity include aluminum nitride, aluminum oxide, and beryllium oxide. This material can quickly and effectively disperse heat away from the surface of electronic components. It also offers mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation.
Discover More: What Is Ceramic PCB? Materials, Types, and Benefits Explained
Ending Notes
Selecting the proper material from the very beginning can effectively avoid failures that would occur later on. The above content has listed the key properties that need to be focused on when selecting a substrate. You should comprehensively consider whether the electrical, chemical, mechanical, and thermal properties of the material meet your needs. Every type of circuit board substrate material has something unique and advantageous. When choosing, you need to weigh multiple factors like cost, performance, manufacturability, and project requirements to determine the best solution.
As an experienced PCB and PCBA manufacturer, UnityPCB can provide various types of PCBs to meet almost every need. We have accumulated rich experience in substrate material selection and can recommend the most suitable substrate solution for you. Welcome to contact us for professional advice.