With technology development, modern electronic products are becoming more and more advanced and diverse. Bare PCB plays a key role in these electronic products. It is a foundation for various components installed. Moreover, it is important to use bare PCB to test before entering mass production, ensuring the circuit board’s reliability. Next, we will give you detailed information about bare PCB and tell you why use it to test.
What Is a Bare PCB?
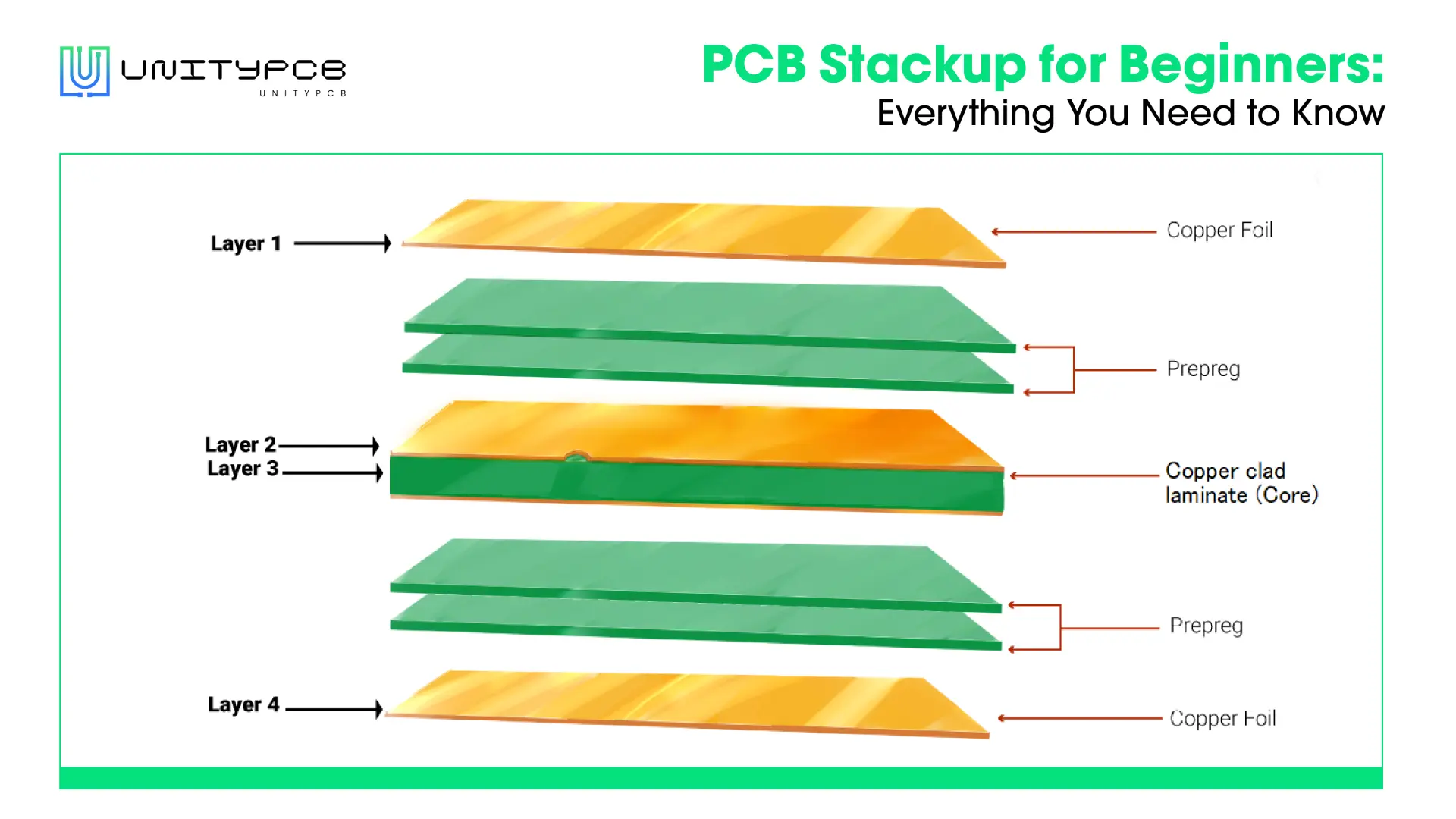
A blank or bare PCB is basically a circuit board that has not yet installed any electronic components. Normally, the basic structure is composed of a substrate, conductive paths, solder masks, screen printing, etc. The bare PCB will provide the conductive traces and mechanical support required by electronic components but cannot function until the components are soldered and installed. It means that in industry terminology, this is called a PCB, which is a circuit board without components installed. After succeeding processes such as soldering and assembly, it will be called PCBA. A PCBA means a complete circuit board that can achieve its intended function.
Bare PCB Defects in the Manufacturing Process
In the bare PCB manufacturing process, there are some defects may occur. Below, we will discuss several defects and explain their influence.
Excessive or Missing Copper Problems
Copper has high conductivity and is often used as a routing material for bare boards to transmit electrical signals. However, excessive or missing copper can lead to circuit board defects. During the etching process, excessive copper may make it difficult for the etching solution to evenly remove the excess, which may cause oxidation corrosion. If the etching process is not properly controlled, the originally designed copper layer may be removed too much, resulting in copper missing problems.
Short-circuit Issues
A short circuit issue is a common defect that occurs when two or more traces are connected that should not be touching. Alternatively, it may be that the traces and pads are incorrectly connected together, causing a short circuit. When testing, you may find that a short circuit causes an abnormally high current to flow through the board. If this defect occurs, you will need to replace the traces so the bare PCB works properly.
Extra Unused Holes
Extra unused holes will take up PCB space, affecting signal routing and component installation. At the same time, this will also reduce the mechanical strength of the circuit board and increase manufacturing costs. By reducing these redundant holes, circuit design can be optimized and performance can be improved.
Why Choose Bare Circuit Boards for Testing?
Using bare PCB boards for testing is a critical quality control step in the PCB manufacturing process, ensuring the reliability of the PCB. Modern PCBs are becoming increasingly miniaturized and multi-layered, bringing more challenges. Even minor defects can cause the entire board to fail. Testing at the bare board stage can detect potential problems (open circuits or short circuits) early, avoiding defects after expensive and fragile electronic components are installed. This is especially true for multilayer PCBs, where repairs are difficult and expensive once the assembly is complete.
In the stage of prototype testing, designers normally take a breadboard or zero PCB for the circuit test. It’s convenient to modify the circuit and make fast experiments but fails to reflect the real situation of a circuit board. You can test the bare PCB before installing the components to verify the circuit. It provides ample opportunity to solve potential problems before the beginning of the mass production process.
Common Types of Bare PCB Testing
Bare board testing is an electrical test performed on a PCB without components installed, mainly including continuity testing and isolation testing. The continuity test is used to ensure that there are no open circuit faults in the circuit and that the current can flow normally. Isolation testing is done by measuring the resistance between two independent electrical connection points. There are two types of testing methods that manufacturers usually apply to test bare PCB.
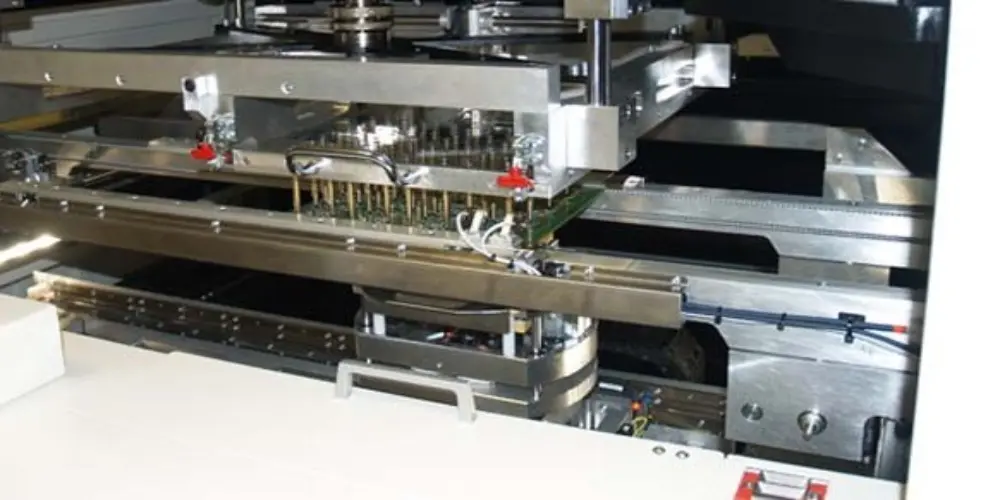

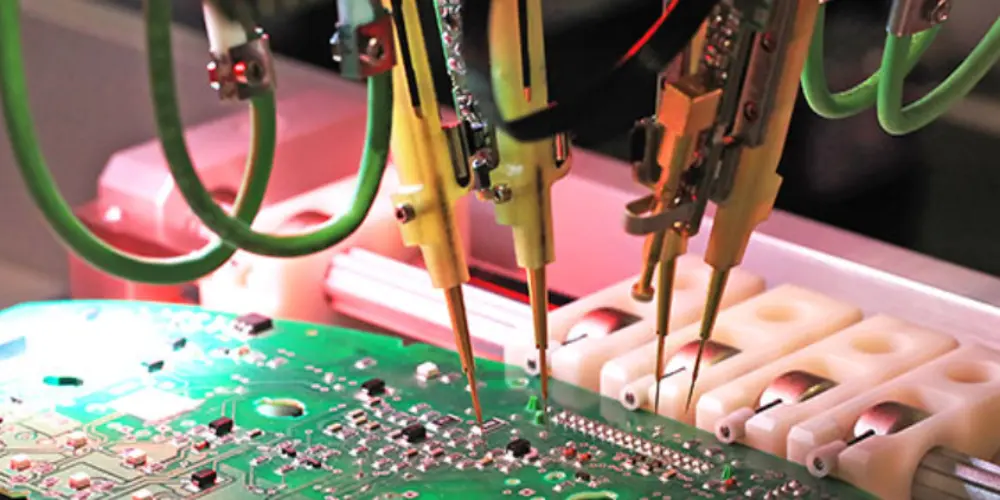
Pinned Fixture Test: Large-volume Production
It is also called in-circuit testing or bed of nails testing, which is an efficient testing method suitable for large-scale manufacturing. This method uses a dedicated test fixture with hundreds of spring-loaded probes to apply pressure through the top and bottom plates to simultaneously detect all connection surfaces on the PCB board. It only takes a few seconds to complete the test, making the testing process more efficient. Of course, this method also has limitations. Each PCB design requires a customized fixture and probe array. This means the initial cost of the test equipment is high. It is also not suitable for testing prototypes and small batches of PCBs.
Flying Probe Test: Small-volume Production
This method employs movable probes controlled by robotic arms that move across the PCB surface. These probes are moved by program instructions that have been set up. Changing over to another PCB design, you can set up another program. The flying probe has to move point by point which is much more time-consuming. It’s a flexible and economical testing method that is suitable for small batch production and the stage of prototype design.
The Advantages of Bare Board Testing
In this part, we provide some benefits of bare board testing, so you can know why to use bare PCB to test before large volume production.
Cost Savings
Bare PCB is easy to test, allowing potential circuit problems to be discovered and resolved early. It avoids discovering defects when expensive electronic components have been installed. This preventive quality control measure can significantly reduce the cost of subsequent repair and maintenance and the loss of components caused by incorrect assembly.
Streamlining the Assembly Process
Perform bare PCB testing at an early stage, which ensures satisfactory PCB functionality. This also ensures the reliability and quality of the PCB, simplifies the subsequent assembly process, and saves time in the later production stages.
Early Defect Detection
Without the obstruction and occupation of components, we can see the layout on the bare PCB more clearly, which can be inspected, evaluated, and tested more easily. We can correct circuit or component-related problems before completing the entire assembly.
Increased Reliability
As PCBs tend to be miniaturized and multi-layered, the density of circuit boards is getting higher and higher. It is difficult to see defects with the naked eye. Testing can ensure that your bare PCB is reliable and capable of soldering expensive components.
Bare PCB vs. Zero PCB: A Detailed Comparison
When talking about bare PCB, you may be confused by the similar term zero PCB. To clear up your doubts, we have compared them in the table below.

| Aspect | Zero PCB | Bare PCB |
| Definitions | Also called Perfboard or DOT PCB, a generic board without predefined circuit connections, layouts, or functions. | Also called blank PCB, a standard PCB without any components installed. |
| Copper Traces or Pads | No predefined copper traces or pads, manual soldering, and connections are required. | Predefined and precise copper traces or pads based on the PCB layout. |
| Solder Mask and Silkscreen | Does not include solder mask and silkscreen layer. | Includes a solder mask and silkscreen layer. |
| Customization | Offers user-driven design flexibility. | Fully customizable during manufacturing to meet specific design requirements. |
| Appearance | Features a grid of perforations. | Specific size with pre-designed PCB layout. |
| Production Process | Simple manufacturing processes. | Requires detailed PCB design files and complicated manufacturing processes. |
| Usage | Used for prototype design, experiment, education purposes, etc. | Commonly used for testing before mass production and as a foundation for component assembly. |
Final Words
Bare PCB is the core of electronic products, highly affecting the quality and dependability of final products’ performance. Applying bare board testing is a key process in PCB manufacturing. Are you looking for a reliable PCB manufacturer? UnityPCB is your best choice. With nearly 20 years of rich experience, we ensure excellent quality in every PCB. UnityPCB has a strict quality control system and advanced testing equipment, using various PCB testing methods to test different aspects of the circuit board, like AOI, in-circuit testing, flying probe testing, etc. Contact UnityPCB right now for high-quality and reliable bare PCB.