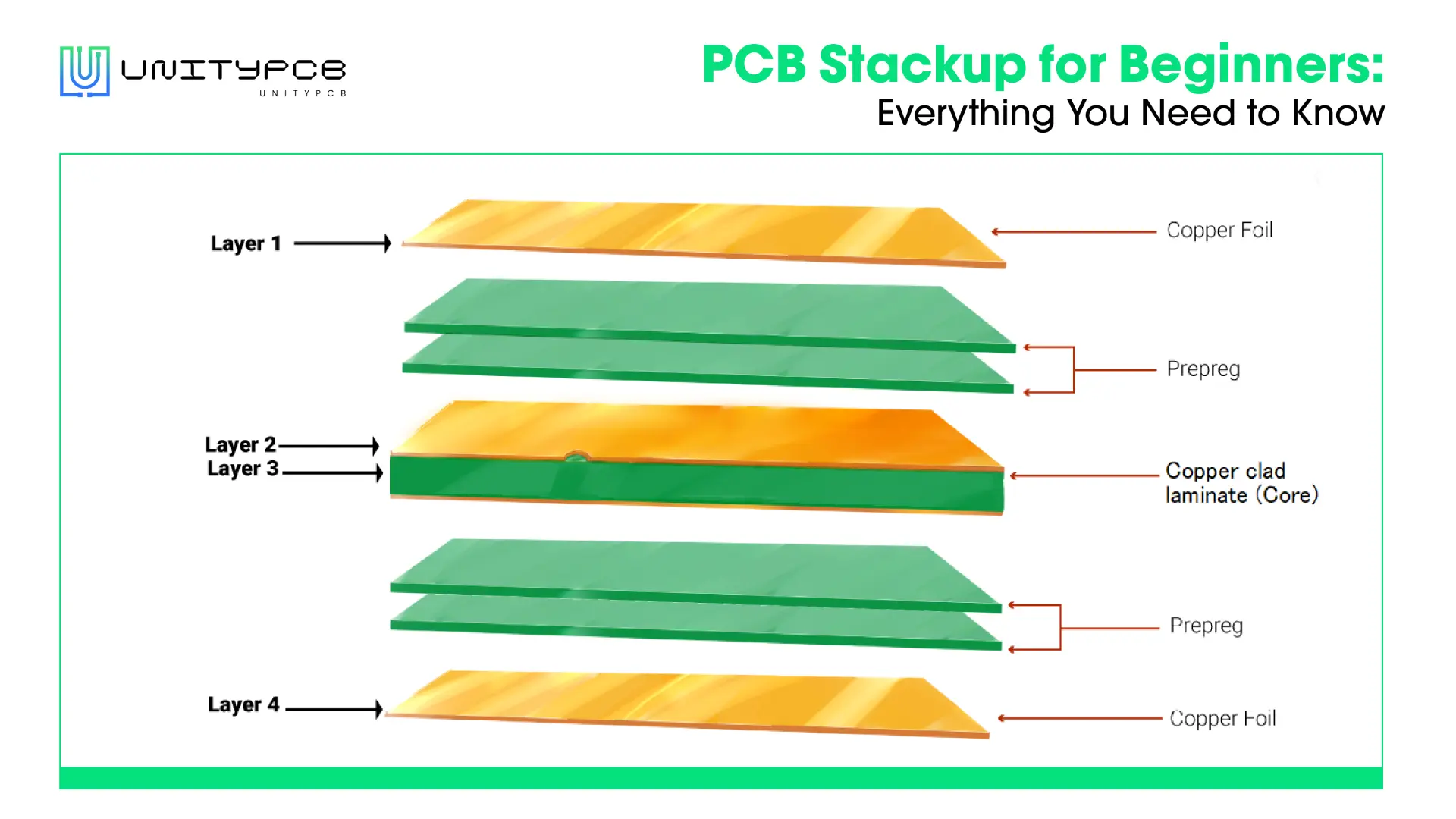
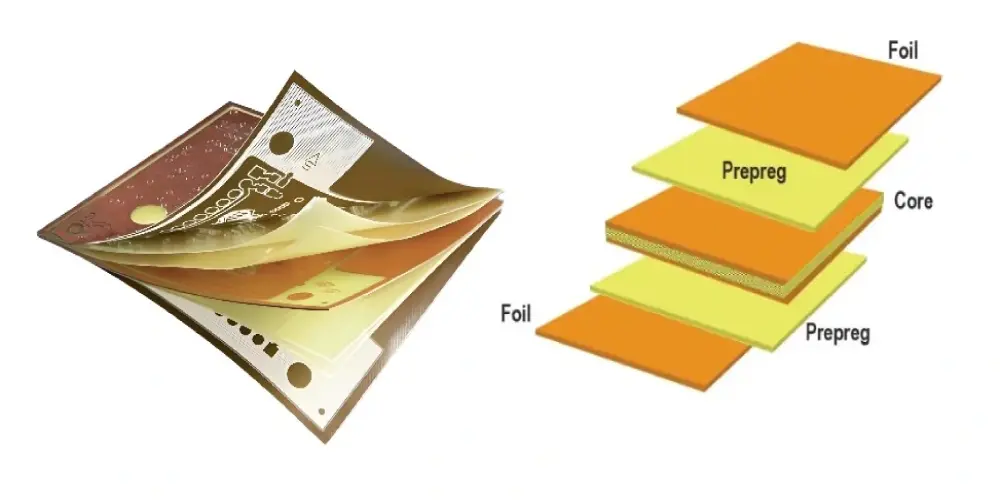
PCB prepreg, short for pre-impregnated, is a dielectric material composed of fiberglass and resin, providing the required insulation and acting as a bonding material. It is an important material in PCB manufacturing, typically sandwiched between two cores or a core and copper foil. This blog dives into PCB prepreg’s properties, types, and key selection factors to help you better understand and make well-informed decisions.
Properties of PCB Prepreg
In this part, let’s discuss the crucial properties of PCB prepreg that are likely to influence the final circuit board.
Dielectric Constant
The stable dielectric constant and low dissipation factor of PCB prepreg are crucial for high-frequency performance. Glass fiber and epoxy have a dielectric constant of around 3.5 to 5, which is acceptable for typical PCBs.
Bond Strength
Bond strength refers to the bonding force between the copper foil and the PCB prepreg layer. A value greater than 2.5 N/mm indicates that there is good adhesion between the two layers that can withstand large external forces and temperature changes without delamination.
Dimensional Stability
Under temperature cycling, the low Z-axis shrinkage and expansion rate of prepreg can prevent PCB via failure as a result of thermal expansion and contraction. The X-Y shrinkage rate is generally in the range of 0.5%, which maintains the overall circuit board’s stability.
Decomposition Temperature
It is the temperature at which a material starts to chemically break down or decompose upon heating. A high Td (> 300°C) indicates the material is stable against decomposition at high temperatures without causing charring.
Moisture Absorption
Low moisture affinity indicates the material has a tendency to absorb moisture, avoiding electrical leakage and reliability issues due to vapor pressure. Typical moisture absorption is typically <0.5%.
Flow and Filler
Sufficient resin flow to fill irregularities in the board while avoiding excess flow. Fillers are typically 15-40%.
Flame Retardancy
High flame retardant PCB prepregs are able to fully prevent circuit boards from catching fire, burning, or producing harmful smoke. UL 94 V-0 grade materials meet high standards of flame retardancy and have better safety.
Types of PCB Prepreg
Different types of PCB prepregs can be suitable for various circuit board requirements. Here are the four most commonly used prepreg materials.
FR-4 Prepreg
FR-4 prepreg is a general-purpose material that offers a balance between cost and performance. It is a glass fiber and epoxy resin composite material that is flame retardant (UL 94 V-0 rating) and has a Tg of 130-170°C (composition dependent). This PCB prepreg is applied to low-frequency digital and analog PCB applications up to several GHz. Due to its stable electrical and thermal properties, FR-4 prepreg is widely used in automotive electronics, consumer electronics, industrial control systems, and telecommunications.
High Tg Prepreg
High Tg prepreg is especially ideal for use in high-temperature resistance and thermal stability applications. It has a glass transition temperature (Tg) that is greater than 170°C or even 200°C. This PCB prepreg uses advanced epoxy resin systems such as bismaleimide triazine (BT) or polyimide and is usually halogen-free and meets environmental standards. Due to its excellent thermal stability, high Tg prepreg can remain stable during lead-free soldering, component mounting, and quality inspection, avoiding warping or delamination problems.
PTFE Composite Prepreg
It is a high-performance dielectric material with a very low dielectric constant (εr) and maintains good electrical and physical properties. Signal loss is significantly reduced compared to standard FR-4, making it ideal for high-frequency circuits. Its ultra-low dielectric constant enables thinner dielectrics and smaller trace spacing, thereby optimizing propagation delay, signal integrity, and impedance control. With these properties, this PCB prepreg is ideal for high-performance microwave and RF applications.
Polyimide Prepreg
Polyimide prepreg has ultra-high temperature resistance (Tg>250°C) and excellent dimensional stability. It can withstand high-temperature soldering (such as lead-free soldering) and high-temperature PCB assembly. With a low Z-axis coefficient of thermal expansion (about 20-30 ppm/°C), the prepreg material can effectively reduce PCB via failures caused by temperature changes. Polyimide prepregs also have excellent flex life durability and can withstand repeated mechanical bending, which is suitable for dynamic bending applications. Despite the high cost of the material, this PCB prepreg is the preferred option in high-demand and extreme environments such as aerospace.
How to Choose Prepreg Material in PCB Fabrication?
When selecting the prepreg material, it’s essential to consider these key factors. Details are below to help you make a correct choice.
Fiber Type
Each fiber has different properties and is suitable for various uses. Glass fiber is the most popular material, with good mechanical and dielectric properties and low cost. Aramid is a solid synthetic fiber that is often used in high-strength circuit boards. Ceramic fibers are mainly used in high-frequency applications and have a stable dielectric constant, but are expensive.
Weave Style
The arrangement of the glass fibers (i.e. woven or non-woven structure) determines some important properties of the prepreg, such as dimensional stability, resin absorption, and anisotropy (the difference in properties of the material in different directions).
Resin Type
Epoxy resin is the most common resin, and other types include polyimides, cyanate ester, and PTFE composites. The choice of resin type depends on thermal properties, electrical properties, cost, etc.
Fiber Aerial Weight
This refers to the weight per unit area of the fiber. Higher aerial weight increases mechanical strength but may increase material cost and thickness.
Resin Content
According to the resin content, prepregs can be divided into standard resin, medium resin, and high resin, and the higher the resin content, the higher the cost. The resin content affects the dielectric constant, thermal expansion, drilling accuracy, and etching accuracy.
Curing Method
Curing determines the final strength and quality of the prepreg. Proper curing ensures optimal bonding, thermal stability, and long-term reliability of the PCB.
Dielectric Constant and Dissipation Factor
When selecting prepreg, dielectric constant, and dissipation factor are the characteristics that must be given special attention in high-frequency applications. Low Dk and low Df materials such as PTFE are used in high-frequency and microwave applications.
CTE
The thermal expansion coefficient(CTE) of the prepreg should be the same as that of the substrate and copper foil to reduce warping and delamination of the PCB under high temperatures.
What Is Resin Flow in Prepreg and How to Measure Resin Content?
Resin flow refers to the resin melts and flows during the heating and pressurization of the prepreg. The resin flow rate is affected by the pressurization and heating rate. Resin content (%) is the percentage of resin in the whole prepreg and determines the thickness of the laminate. The resin content (%) is usually measured by the combustion method which can be calculated using this formula. Weight loss is obtained by subtracting the final weight after combustion from the initial weight.
Resin (%)=Weight Loss/Initial Weight x100%
Best Practices for Storing and Maintaining Prepregs
Proper storage and handling of prepregs are essential to maintain their performance and extend their shelf life. In this part, we look at some best practices to ensure optimal performance of the materials throughout their lifecycle.
Original Packaging: The PCB prepregs should be stored in their original packaging and the packaging needs to be sealed to prevent moisture absorption and evaporation.
Orientation and Cleanliness: When placed, they should be stored sideways or vertically to prevent creases in the material. The storage area also needs to ensure that there are no potential pollutants.
Temperature and Humidity: The pre-impregnated materials are usually stored in a dry and shady place with a temperature range of 15-30℃ and a relative humidity of 30-60%.
Light Avoidance: The PCB prepreg materials need to be protected from UV and sunlight during storage and use, which can cause polymerization reactions.
Inventory Rotation: PCB prepregs have a shelf life and will degrade over time. Regularly rotate the PCB prepreg inventory, which can be rotated using first in, first out inventory. Generally, it’s best to use them within six months after purchase.
Prepreg vs Core: What Are the Differences?
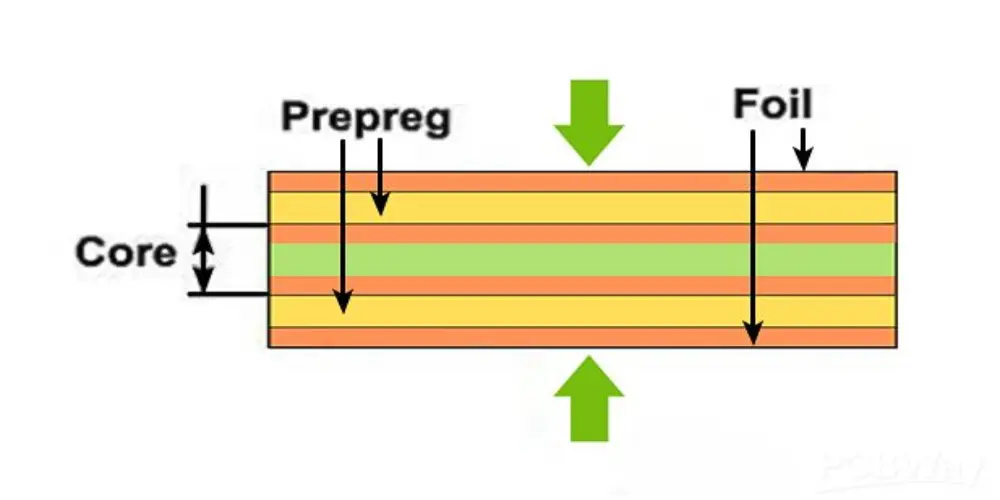
Due to the similarities between prepreg and core, confusion often occurs between them. Prepreg is a semi-cured material made of glass fiber and resin, which acts as a binder to bond the core during the lamination process. The core is one or more prepreg laminates, which are pressed, hardened, and heat-cured to form a fully cured rigid laminate with copper layers on both sides, providing mechanical strength and electrical connections as the basis of the PCB. In simple terms, the core is a prepreg and laminate product, and its rigidity is greater than the prepreg. Below is a comparison table to distinguish more easily.
| Aspect | Prepreg | Core |
| Composition | A semi-cured material consisting of woven fiberglass impregnated with resin. | A fully cured, rigid laminate with copper layers on both sides. |
| Functionality | Provides insulation and bonds core layers together during lamination. | Acts as the foundational structural layer of the PCB. |
| Curing Process | Semi-cured, flows and solidifies under heat and pressure during lamination. | Fully cured, remains unchanged during lamination. |
| Dielectric Properties | Vary before and after lamination. | Remains stable. |
| Stackup location | Placed between two cores or between a core and copper foil. | Typically positioned in the middle of the PCB. |
| Physical Structure | A more malleable structure before lamination. | Rigid and fully cured, with copper foils bonded on both sides. |
Ending Notes
PCB prepreg selection can strongly impact the performance and manufacturability of circuit boards, especially for multilayer PCBs. Key parameters such as resin type, resin content, and weave styles directly influence the mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties of the prepreg material. With a full understanding of prepregs and their characteristics, PCB designers can make better decisions tailored to specific application requirements and manufacturing processes while minimizing potential issues during fabrication.