PCB assembly refers to the process in which the components are installed on the printed circuit board. This process involves multiple steps to ensure reliable soldering and PCB performance. From initial preparation to final circuit board cleaning, each stage plays a key role in achieving a high-quality PCBA. In this blog, we’ll walk you through these essential steps and provide insight into how each stage contributes to the success of the PCB assembly process.
PCB Assembly Process: 8 Key Steps Explained
Sufficient preparation before PCB assembly can ensure efficiency in the whole process. DFM checking is necessary prior to the production stage. Problems that may affect function or manufacturing, such as defects in small component spacing, can be identified by reviewing the PCB design files and related instructions. Performing an early inspection can ensure the quality of a product and cut down scrap rates to reduce the cost of production and additional expenses. Next, we go on to introduce the process steps of the assembling procedure.
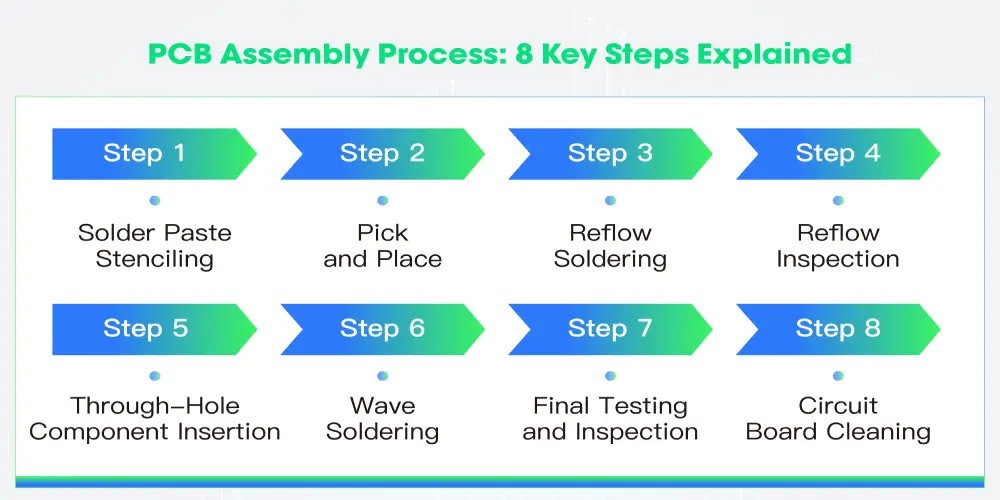
Step 1: Solder Paste Stenciling
Check the stencil to make sure it is correct. Then, using a stencil allows accurate deposition of solder paste on the intended area of the PCB. Solder paste is a mixture of solder (composed of powdered metal solder such as tin, silver, copper, etc.) and flux.
Step 2: Pick and Place (SMT Components)
Then, the circuit board is sent to pick and place machines which generally install SMD components such as BGAs and ICs. The machine will automatically pick up the component and rotate it to the correct orientation for placement on the preprogrammed locations of the circuit board.
Step 3: Reflow Soldering
After component placement is complete, the board is put through the reflow oven. This is only used for SMT assembly. The solder paste melts and after cooling, it firmly connects the component and the pad. The reflow temperature of solder paste is usually 180-220℃, and the temperature of tin-free solder paste is 210-250℃.
Step 4: Reflow Inspection
Completing the above SMD component installation does not mean that the PCBA is complete. The PCBA with installed components needs to undergo various tests. During the reflow soldering process, the solder joints may have poor connection quality or no successful connection. These defects can be identified by below several testing methods.
Manual Inspection: SMD components are small and difficult to check for alignment and identify defects with the naked eye.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): AOI systems inspect PCB solder joints and components from multiple angles through a high-powered camera array. It can quickly identify defects such as missing components, poor soldering, and misplaced components. This automated inspection method is particularly suitable for high-volume PCBA production and can judge the quality of soldering by observing the light reflection of the solder joints.
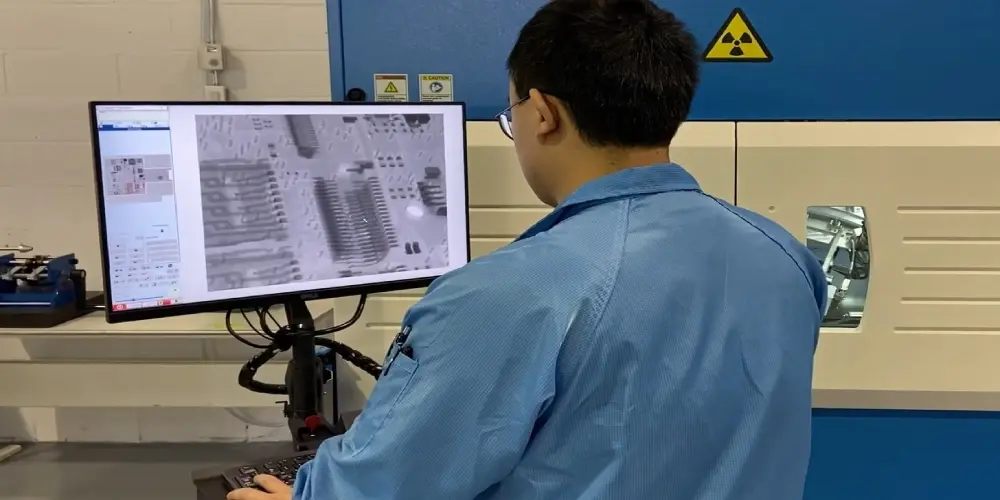
X-Ray Inspection: This is a non-destructive test technology. It primarily serves to identify the internal structure of multi-layer and complex PCBs. The X-rays can penetrate through the PCB layers and may reveal defects hidden beneath components or inside multilayer boards.

Step 5: Through-Hole Component Insertion
According to the PCB design file, the technician manually inserts the components onto the board. Verify that they are placed precisely. If the component position or orientation is wrong, it is very easy to correct it immediately.
Step 6: Wave Soldering
The board then passes over a wave of molten solder at a high temperature after component insertion. The solder contacts and wet the leads and pads of the components. When the board leaves the solder wave and cools, a strong solder joint is formed.
Step 7: Final Testing and Inspection
After completing the PCB assembly, the circuit board needs to undergo a final inspection, such as open circuits, short circuits, missing components, soldering defects, etc. Below are two commonly used testing methods.
Functional Test: This testing detects whether its electrical characteristics (current, voltage, signal output, etc.) meet design specifications by simulating the actual operating environment of the PCB. If these parameters are found to fluctuate abnormally or exceed the predetermined range during the test, the PCB will be judged as unqualified and recycled or scrapped.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT): This method uses probes to directly contact the test points on the PCB board to perform electrical tests on each component. This test method can be quickly and automatically tested.

Step 8: Circuit Board Cleaning
The assembly of a PCB is quite a dirty process. Most likely, there could be some dirt or flux on the circuit board surface. After all soldering and testing are done, this is a very important step for cleaning. Deionized water does not have the ions in ordinary water that would affect the circuit boards. The washing using deionized water is quite efficient for removing flux residue and contaminants from a PCB. Afterwards, it is quickly dried by compressed air.
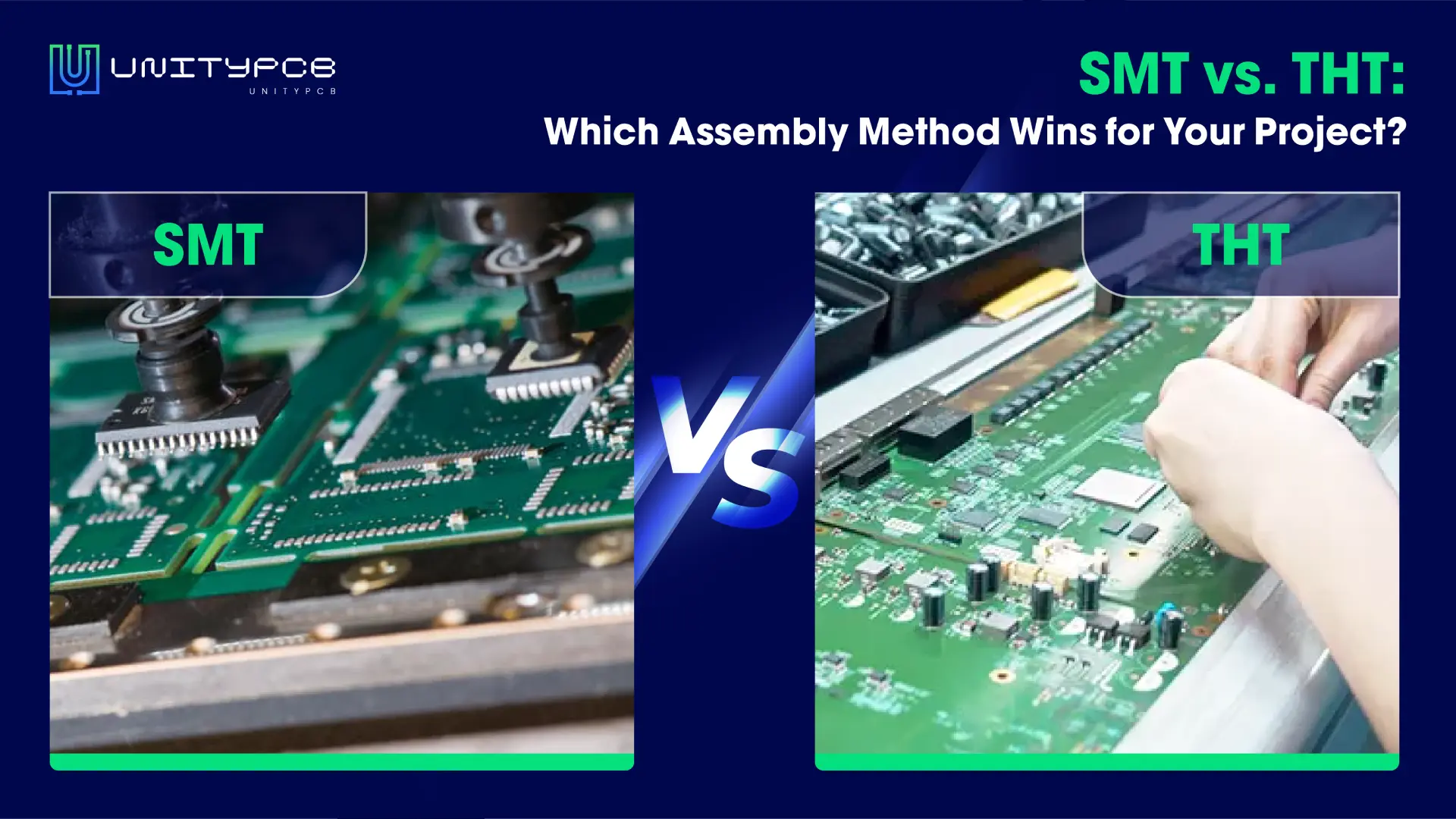
Types of PCB Mounting Technologies
There are three types of approaches used in PCB assembly for SMD or through-hole component installation. Here are the specifics.
Surface Mount Technology
SMT is a technology that automatically places electronic components on a circuit board and connects them through a reflow soldering process. This technology is suitable for small, light, and sensitive components and allows for denser component layouts, effectively improving the integration and manufacturing speed of circuit boards.
Thru-Hole Technology
THT refers to the PCB assembly method of inserting the electronic components’ pins or leads into holes on the PCB. After that, connect the pins or leads of these components to the pads by hand or wave soldering. It is suitable for large components or small batch and prototype production.
Mixed Technology
Nowadays, electric devices are increasingly complex and tend to be integrated and miniaturized. It is common for a circuit board to contain both SMD components and through-hole components. Soldering is a complicated process and is affected by many factors. A mixed soldering technique of the two techniques mentioned above is usually used.
SMT vs. THT: A Comparison of PCB Mounting Methods
| Aspect | SMT | THT |
| Components Size | Smaller components, suitable for miniaturization | Larger components, less suitable for miniaturization |
| PCB Space Utilization | High-density mounting, saves space on the PCB | Requires more space due to larger components and holes |
| Soldering Method | Reflow soldering | Wave soldering or manual soldering |
| Mounting Process | Components are mounted directly onto the PCB surface | Components are inserted through holes in the PCB |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower mechanical strength, less durable under stress | Higher mechanical strength, more durable under stress |
| Assembly Speed | Faster assembly process, suitable for automation | Slower assembly process, less suitable for full automation |
| Repairability | More challenging to repair or rework | Easier to desolder and replace components |
| Manufacturing Costs | Lower due to automation | Higher due to manual labor and drilling |
| Applications | Ideal for compact, high-performance devices (e.g., smartphones, laptops) | Suitable for high-reliability applications (e.g., industrial, automotive) |
Tips for Successful Printed Circuit Board Assembly
Now, you have learned that the PCB assembly process involves many steps. The following tips will help you achieve successful PCB assembly.
- Providing an accurate BOM to avoid purchasing mistakes and assembly errors.
- Purchasing high-quality components from reliable suppliers.
- PCB prototypes can be built for testing before assembly.
- Strictly controlling workshop temperature and humidity to meet the process requirements.
- Collecting the production data and product quality feedback in time to optimize the process parameters and procedures.
Choosing UnityPCB as Your PCB Assembly Service Provider
PCB assembly involves a series of steps that are essential to creating a successful and reliable electronic product. Therefore, choosing a reliable PCBA service provider is very important. UnityPCB will be your perfect choice! With nearly 20 years of production experience, we are committed to providing one-stop PCB & PCBA services. UnityPCB has strict testing, advanced technology, and top certification to ensure that every PCB & PCBA meets the highest standards. Our advanced production lines and streamlined manufacturing processes ensure fast and on-time delivery. Contact us for a quote and we will provide you with professional services.