What you probably didn’t know is that the function of the regular electronic devices you use in your home is determined by the PCB components that are mounted on the circuit board. Printed circuit boards contain several components which are interconnected to accomplish a particular task. Awareness of these components gives further to perceive how electronic apparatus do various activities. This article will focus on 9 common PCB components and their functions.
What Are PCB Components?
PCB components are different individual parts that are assembled on an empty circuit board, which makes up one complete circuit board. All these PCB components make significant contributions to the general operations of the PCB, enabling the device to perform specific tasks in a variety of electronic products. Every component is unique as it possesses its attributes and performs a specific role. Common components like diodes, resistors, capacitors, and so forth.
Understanding 9 Common PCB Components and Their Functions
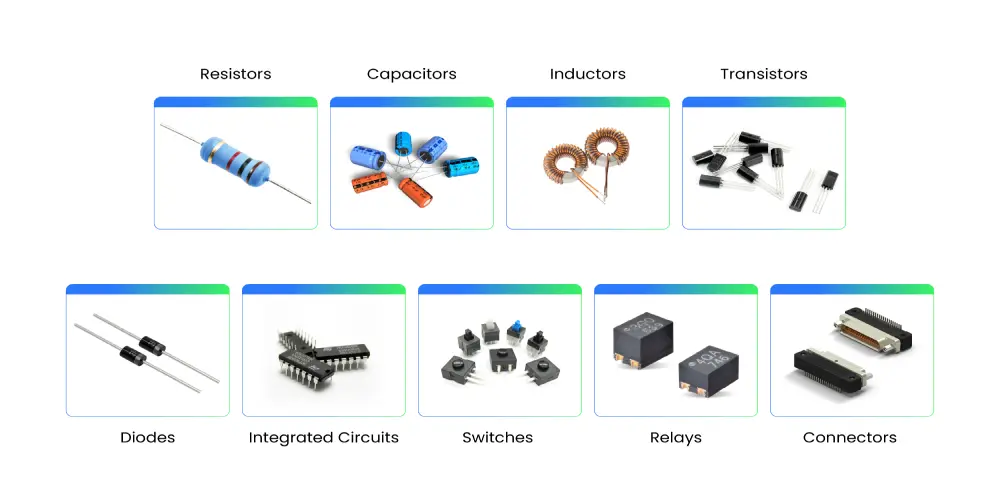
There are a variety of electronic PCB components assembled on the board to process different functions. Below we will deeply explore 9 common PCB components and their functions.
1. Resistors
A resistor is a component in a circuit that helps in controlling the flow of electric current. It performs mainly the function of a voltage divider and a shunt, regulating as well as stabilizing voltages and currents.
Variable resistors have the capability of varying their resistance while fixed resistors do not have the feature of varying their resistance. Notably, variable resistors are components that enable the user to vary the circuit which is very crucial in devices that control volume and light intensity. Usually, it is an oval-shaped body with green or blue stripes and the “R” symbol on it.
Film Resistors: They are made out of a thin film of metal or carbon that acts as a resistive layer, around a ceramic core. It’s an ideal component for devices with high stability, high accuracy, and low noise, such as medical and audio equipment.
Thermistors: Variable resistors, which are frequently found in thermometers and rechargeable batteries, control voltage in reaction to temperature variations.
2. Capacitors
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating charges of opposing types in two conductors. A substance called dielectric fills the space between them. It holds the charge within the circuit board and releases it whenever there is a need to supply power elsewhere. In its physical form, most capacitors have a small cylindrical shape and are commonly marked with numerical markings. They are useful parts that are employed in circuits that are intended for filtering, coupling, bypassing, and tuning.
Ceramic Capacitors: It is one of the most popular capacitors. Because of its low cost, small size, and comparative stability, it can be used in a variety of different applications.
Film Capacitors: It is suitable for high-frequency applications due to its high stability and reliability and low dielectric loss.
3. Inductors
An Inductor is a part that, like a coil, stores energy in a magnetic field when current passes through the part. It can also store electrical energy by converting it into magnetic energy. We can find that both the magnetic field and the inductance increase in proportion to the number of coils. As well as filtering noise and screening signals, inductors may also decrease electromagnetic wave interference and regulate current.
Air-core Inductors: These inductors have no core, take more turns than those inductors with cores, and can be best used when low inductance is desired. It is typically applied in filter circuits and high-frequency applications.
Toroidal Core Inductor: A piece of wire is wrapped around a circular core, which is usually a ferrite. It is widely employed in medical devices, switching regulators, and industrial controllers.
4. Transistors
Transistors are tiny semiconductors that function as switches as well as amplification and control of electrical signals. When it works as an amplifier, it can take a small input current and turn it into a larger current output. It functions as a switch to determine whether an electrical signal goes through the circuit. In integrated circuits, which are composed of several transistors and circuits, transistors are the fundamental elements.
Bipolar Junction Transistor: It is also called BJT, which gets its name from the fact that it has two PN junctions. It is a component with the ability to regulate the current.
Field-effect Transistor: A Field Effect Transistor, abbreviated FET, is a three-terminal unipolar semiconductor device that controls voltage.
5. Diodes
A diode is an electronic device made of semiconductor material with two electrodes, positive and negative. It only permits one direction of current flow. By doing this, the current cannot flow in the incorrect direction. The most common diode is the LED, called Light Emitting Diode.
Switching Diode: It is used to open and close the circuit, and the operations are controlled by the application of voltage in different directions.
Light-emitting Diode (LED): While current passes through a semiconductor it produces visible light directly by converting electrical energy into light.
6. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Integrated circuits are complex components consisting of many transistors and other required PCB components combined into a single semiconductor chip. It is a miniature structure with the desired circuit function. Electronic components are now more intelligent, highly reliable, low power consumed, and micro-miniaturized thanks to integrated circuits.
Linear ICs: Linear ICs are uncomplicated and normally the amount of components incorporated within such an integrated circuit is minimal. They are used mostly for audio & RF amplifiers and temperature sensors.
Digital ICs: They have only two different states of signals and are usually incorporated in computers, memories, and so on.
7. Switches
The main thing about switches is that they function to control whether or not current can flow. Through the use of an open or closed circuit switch, it regulates the current flowing through a circuit. It comes in many forms, toggles, sliders, levers, rotary, push buttons, keys, etc.
Fused Switches: It is a fuse integrated into the switch that acts as a protection.
Electrical Switches: It is used to connect circuits and control switches with electrical signals.
8. Relays
A relay is also a switch, an electromagnetic switch. It works by electromagnetic induction, when a relay is energized, a magnetic field is created to attract a contact, a circuit closure within the relay. It protects the circuit from excessively high voltages or currents so that the circuit can operate safely.
Electromechanical Relay: It is the most basic type of relay and works by controlling an electromagnet ring of movable contacts, a physical movement that takes much longer.
Solid State Relay: It controls the switching of relays through semiconductors operates faster and lasts longer than solid state relays.
9. Connectors
Connectors are components that are employed for making an electrical interconnection between various PCB components, circuit boards, or devices to enable the passage of data and signals. They can be used temporarily or can be fixed as per the requirement of the consumer and the manufacturer. It consists of two basic parts, the contact and the case. The housing is present to physically safeguard and guarantee the integrity of a link.
Card Edge Connectors: They are located typically close to the edge of the board and enhance high signal integrity on the board. Many of these connectors are typically incorporated into computer gear. It assists in relaying signals between the printed circuit board and external PCB components.
Audio/Video Connector: It is primarily used to carry signals for video and also audio. These connectors can be used in a single audio channel signal as well as multiple audio channel signals. Audio connections may be provided in the form of plugs, jacks, or a combination of both.
How to Identify Components in Circuit Boards
1. Visual Identification
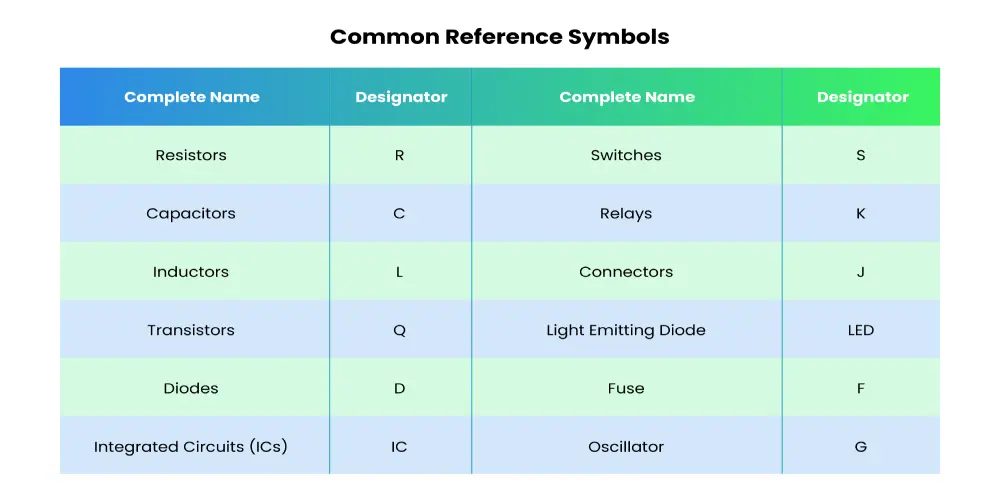
Components Designator: Many printed circuit boards have reference marks for various PCB components printed on the surface for easy identification. Some common reference symbols are listed in the table below.
Components Shape and Marking: Different PCB components have distinct shapes, and you can identify some common components by their shapes. For example, resistors are usually rectangular or cylindrical in shape and have color-coded ribbons on their surfaces that indicate the resistance value. Numbers on capacitors represent their capacitance.
2. Equipment and Tools
Multimeters: It is a measuring instrument that can test a wide variety of electrical characteristics. They can be utilized to test resistance, voltage, and current and can correspondingly help determine the state of PCB components.
Oscilloscopes: They can recognize transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits. Observing waveforms and signals is also helpful when carrying out the identification of PCB components since it helps one understand the function of the component.
Other Equipment: LCR meters and component testers can also be used to verify and identify components, including semiconductor parameters, inductance, and capacitance, by giving comprehensive identification information.
3. Reference Documentations
You can find a blueprint of the printed circuit board layout and component details by referring to the schematic and components data sheets.
4 Tips for Choosing PCB Components
Recognize Performance Needs
Consider the performance requirements of the device, which encompass a variety of factors such as temperature ranges, ambient conditions, voltage, and current levels, among others.
Cost Consideration
Pricing is something that one has to consider when choosing PCB components. It means that components with high cost and good performance levels tend to add to the total cost. However, we can choose low-cost materials that can be effectively used in the production line without having to compromise the quality of the final product.
Choose Reliable Components
Printed circuit board performance and service life are related to the quality of the PCB components installed in the products. Dependable components guarantee that the printed circuit board will work in the way it is supposed to.
Assembly Technology
When choosing PCB components compatibility with the assembly process is also an important factor. For instance, some of the components like high-power inductors are not compatible with surface mount technology.
Summary
The ability to identify and differentiate the basic components of a circuit board is important for anyone who wants to understand how electronics work. All of them have a crucial, but not the same, role in the performance of their work in the circuit. With the help of this knowledge, you may have a deep understanding of PCB components. As technology evolves, more better and higher performance components will emerge and assemble on the board to run in a wide range of applications.