In order to guarantee the dependability and quality of electronic devices, PCB testing is a crucial step in the manufacturing process. Printed circuit board complexity increases along with technological advancement, while performance and functionality both improve at the same time. In order to detect difficult-to-find flaws and confirm excellent performance, efficient PCB testing techniques are required. PCBs can be inspected using a variety of techniques, ranging from straightforward visual inspection to complex automated methods, individually or in combination, to make sure they meet design specifications and function as intended. Discover 7 popular PCB testing techniques in this article to learn how to test circuit boards efficiently.
Why Does PCB Inspection Matter for the Manufacturing Process?
Saving Cost
Completing PCB testing early in the printed circuit board design process can reduce defects that occur during the production process. Use prototype PCB or small-scale PCB assembly testing to resolve defects before mass production. It can obviously decrease the production cost. Moreover, improving product reliability will ultimately reduce return rates, thereby reducing the costs associated with dealing with defective products with customers. Product recalls, replacements, and repairs can be expensive when they occur.
Guaranteeing Product Reliability and Safety
Failure of the circuit board can cause electronic equipment to malfunction, which can cause significant safety issues. Especially in key equipment used in medical equipment, automobiles, and aerospace fields, the reliability of circuit boards is particularly important. The failures in these applications can lead to serious safety accidents, so PCBs must be rigorously tested.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
PCB testing can identify problematic products, reduce the number of problematic products entering the market, further reduce customer complaint rates, and improve customer satisfaction. There is a high level of customer satisfaction with the products, and there has been an improvement in the company’s reputation, brand awareness, and product image.
Meeting Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have standards and requirements for the quality and performance of electronic products. PCB testing can ensure that products meet the standards of these industries and comply with regulatory requirements.
7 Common PCB Testing Methods
Now that we know the importance of PCB testing, how should we test PCB? Check out the following 7 common PCB testing methods.
1. Visual Testing
Visual inspection is a common PCB testing method. This process can detect some obvious circuit board errors such as incorrect component placement and physical damage. It helps in recognizing some issues impacting the reliability and performance of PCB. Visual testing can be viewed as a lower-cost type of inspection. However, this approach is unreliable, and in some cases, the problem can only be identified by machines.
2. In-circuit Testing
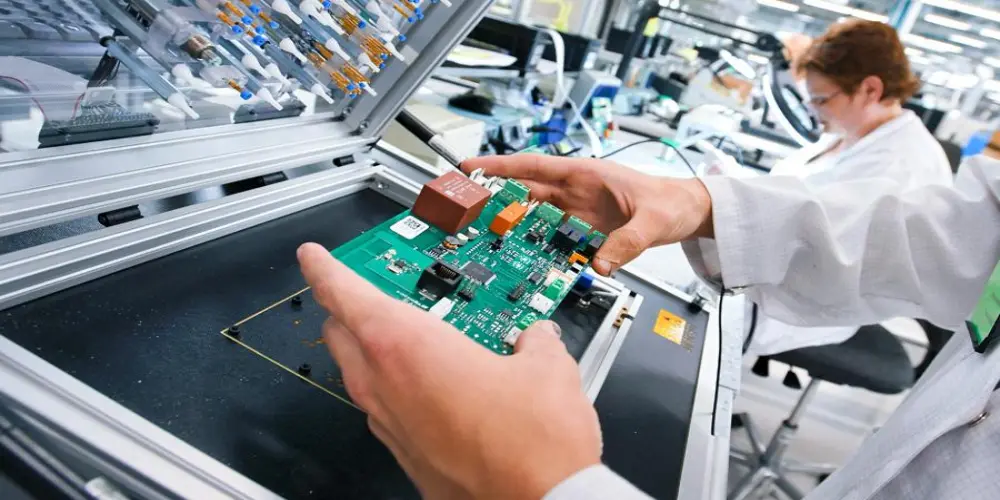

In-circuit testing (ICT) requires powering on and starting each circuit on the PCB for detection. It is composed of many actuators and sensors and uses a flying probe to move freely to connect circuits on the board for detection. The probe is controlled by software, revising according to different PCB layouts using the same testing system.
The goal of this PCB testing is to ensure that every single component that must be installed on the board is placed correctly and all of them are capable of doing what they are designed for. Otherwise, it can check for the circuit detects like opens or shorts.
This is an automatic detection system that is efficient in the detection of most faults. However, it will need special equipment to process testing and the detection cost will be expensive relatively. Therefore it is best used in large-scale, and more developed products.
3. Flying Probe Testing
Flying probe testing (FPT) does not require custom test fixtures, so the total test cost is reduced. A fixture holds the printed circuit board in place, and the test pins are controlled by software to test the relevant points on the board. Compared with ICT, flying probe testing does not require powering the PCB. FPT is commonly used to check short circuits, resistance, inductance, capacitance, diodes, and transistor orientation.
This PCB testing can match different circuit boards more quickly through simple programming, but the testing speed is slower than ICT. It is frequently used for prototype and small-scale production PCB inspection.
4. Automated Optical Inspection
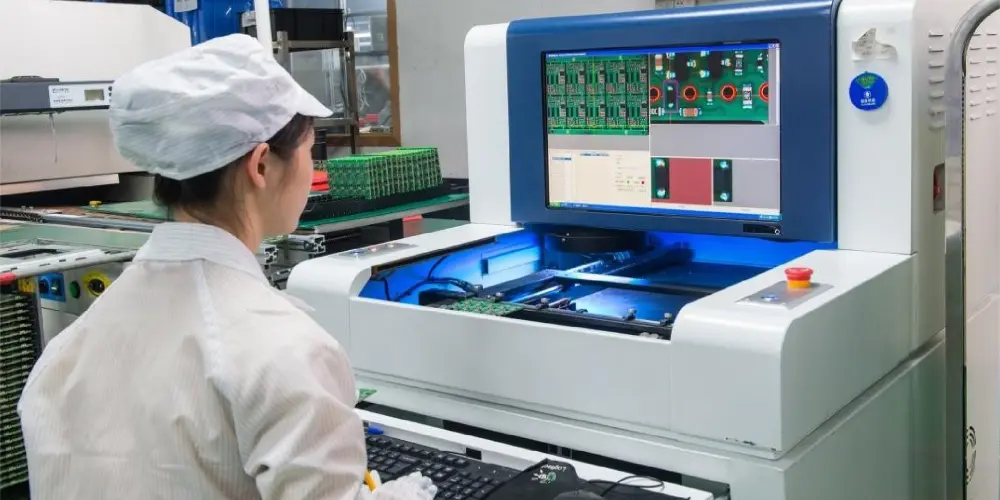

Automated optical inspection (AOI) employs a camera and a microscope to capture an image of the circuit boards. The image is then compared with the circuit board schematic while evaluating noncompliance with the schematic during the process.
This PCB testing can reveal the following issues, under or over-etching, excess solder, and solder gaps. It can identify when components are missing, incorrectly placed, and out of alignment. AOI can also identify short and open-circuit issues and lead faults on the circuit board.
The PCB is not powered during the AOI inspection. Not every component inspection can be covered by this method. It must be used in conjunction with other PCB testing methods like FPT or ICT.
5. X-Ray Inspections
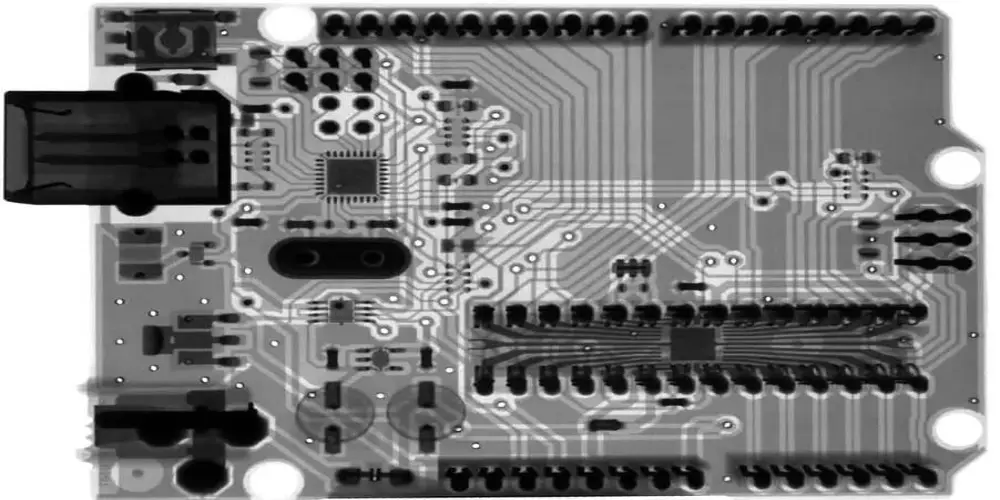
X-ray Inspection is a technology whereby X-ray photons pass through a material and form an image on the opposite side. The physical properties of the material are different, and essentially different numbers of photons are accumulated on the other side, and hence an image is produced.
Heavier materials absorb more X-rays and appear darker in images than materials that absorb less. In an X-ray image, the metal of a PCB appears dark, while other materials such as glass and ceramics appear transparent. This is very effective in detecting circuit board problems such as opens, shorts, inaccurately placed, and missing components.
This technology can find hidden errors that are not easy to find, such as solder bridges, solder voids, pin-hole fills, and solder shorts. Especially for high-density PCBs, they are very small and the components are densely assembled. These problems are difficult to detect manually or using other detection methods. X-ray is an effective method and does not damage the circuit board.
6. Burn-in Testing
The burn-in test is an intensive and extreme test that puts the PCB in extreme environments and continuous working conditions to test its performance. During this testing process, performance data or existing problems can help engineers find out the cause of the failure and make optimizations.
This is not a mandatory test. It is applicable to electronic products that require better performance and reliability, or products that need to operate in harsh environments. One thing that needs to be kept in mind is that burn-in testing may shorten the service life of printed circuit boards.
7. Functional Testing
Functional testing mimics the final electrical conditions of the PCB and checks the operation of the entire PCB as well as the different components. This often is the last testing in the manufacturing process to confirm whether the PCBs work or not in the given electronics products.
This PCB testing method can also detect circuit anomalies, such as whether voltage and current are correct. There are so many reasons that would lead to a wrong voltage and current supply to a circuit which may be due to a wrong component or missing component.
This type of testing looks at the products as a whole and tests whether they function properly. It does not detect problems with specific components or details. So it doesn’t apply to PCB prototype testing. Functional testing can be manual, semi-automatic, or automatic, depending on the complexity of the PCB.
Last Words
We looked at seven popular PCB testing in this blog, each with advantages and limitations. The complexity of the PCB design, test costs, production volume, and usage requirements all influence the test method selection. Manufacturers can decrease costs and increase testing efficiency by appropriately using them individually or by combining these test methods. In a market where competition is escalating, knowing and utilizing the latest testing methods will guarantee that your printed circuit boards retain their superior performance and dependability.