Knowing the distinction between PCB and PCBA is essential for anyone employed in the electronics industry. At first glance, they may seem interchangeable and similar, but they represent different stages in the electronics manufacturing process. This guide seeks to clarify the distinctions between PCB and PCBA, exploring their main parts, and more. After being equipped with this knowledge, you will have a better understanding and know how to differentiate between PCB and PCBA.
What Is a Printed Circuit Board? (PCB)
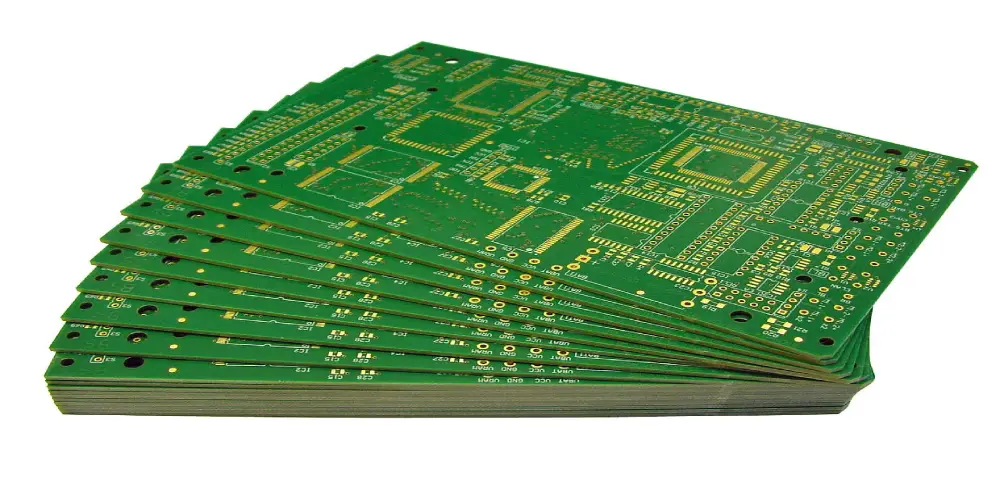
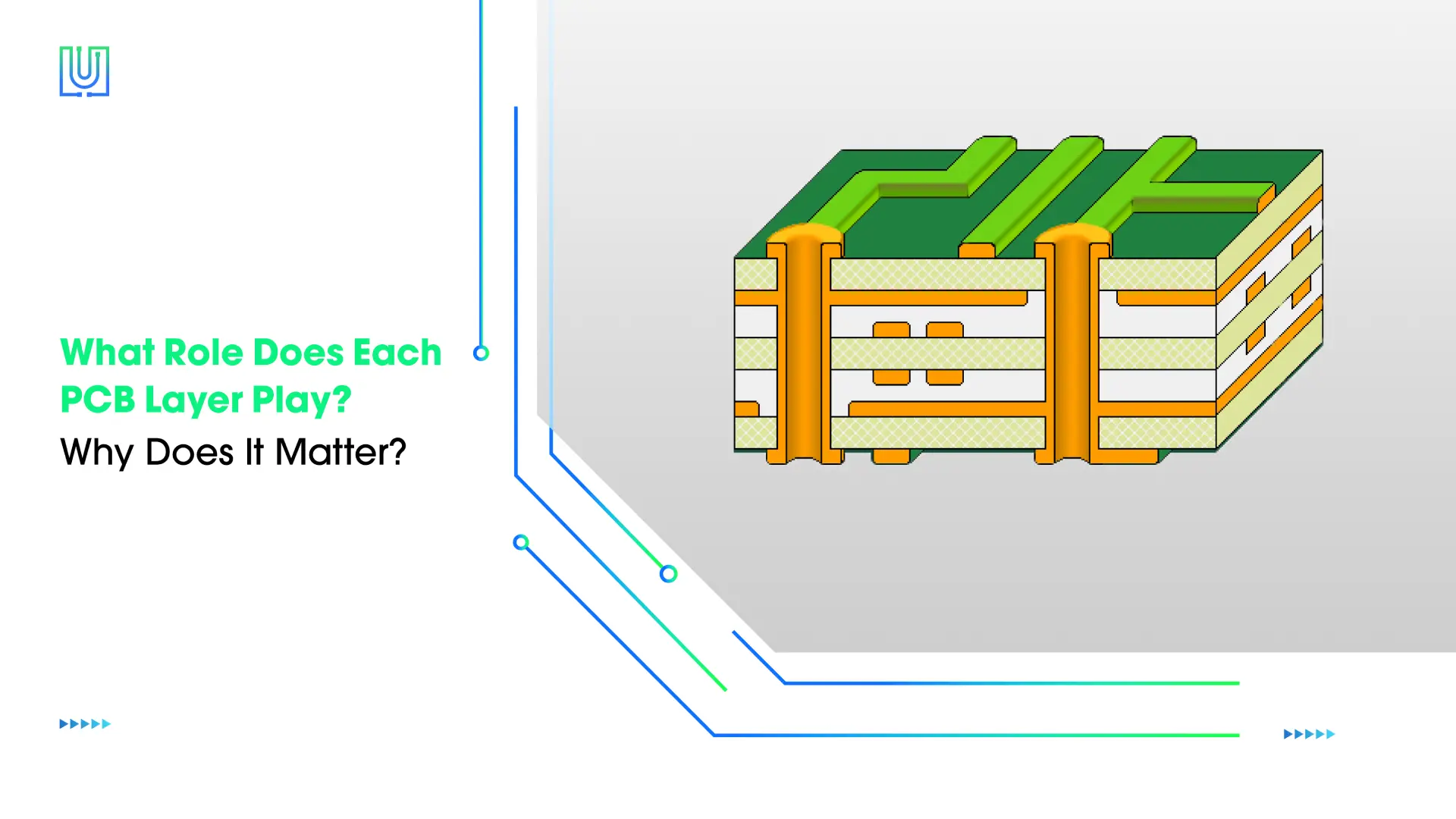
A PCB is a bare printed circuit board that acts as a mechanical support board on which components can be mounted. Its substrate is made of non-conductive material, and conductive traces and pads are etched on the surface of the conductive layer. The non-conductive layer is usually made of FR4 and polyimide, which are insulating, waterproof, and stable. Copper has high conductivity and is usually used as the conductive layer.
What Are the Main Parts of PCB?
Insulating Substrate: It is usually made of insulating material and provides mechanical support and electrical insulation for the PCB. The commonly used material is FR-4, and different materials such as ceramics and metals can also be used according to different performance requirements.
Conductive Layers: The conductive layer is laminated on the substrate and is etched and electroplated to form traces and pads that can transmit electronic signals and provide a place for electronic components to be mounted. Copper is generally used as the conductive layer.
Solder Mask: This is a layer of epoxy resin coating that covers all the areas except the pads where soldering is required. Its function is to prevent copper layer oxidation and short circuits. At the same time, it can also prevent the formation of solder bridges between pads, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of soldering.
Silkscreen Layer: The function of this layer is to mark the location, model, direction and other information of the components to facilitate subsequent component installation and maintenance.
Drill Holes: Drilling holes on the PCB are used to install electronic components and realize electrical connections. They can be blind, buried, or through holes.
Vias: The holes on the PCB can achieve electrical connection between different conductive layers, allowing electronic signals to be transmitted in multi-layer PCBs.
Edges: On the edge of the PCB, it can be used to install connectors and connect external devices and other circuit boards. It looks like a shiny gold terminal.
Pads: These pads are used to mount electronic components, and their size and shape are usually designed according to different electronic components.
Different Types of PCBs
PCBs come in three primary varieties: Single-layer PCB, Double-layer PCB, and Multilayer PCB.
Single-layer PCBs: This is a relatively simple circuit board, it has only one conductive layer. This kind of circuit board is simple and cost-effective, suitable for some simple electronic toys, etc.
Double-layer PCBs: Double-sided boards have conductive layers on both sides, and components can be mounted on both sides, allowing for more complex and dense circuit designs. Compared with the single-layer board, it is more flexible and smaller.
Multilayer PCBs: Multilayer PCBs have multiple conductive layers and insulating layers that are laminated together. Through holes are made on the PCB board, and then the conductive layers are electrically connected. The complexity of the circuit boards increases with the number of layers, and these boards are more suitable for high-performance electronic products.
What Is a Printed Circuit Board Assembly? (PCBA)
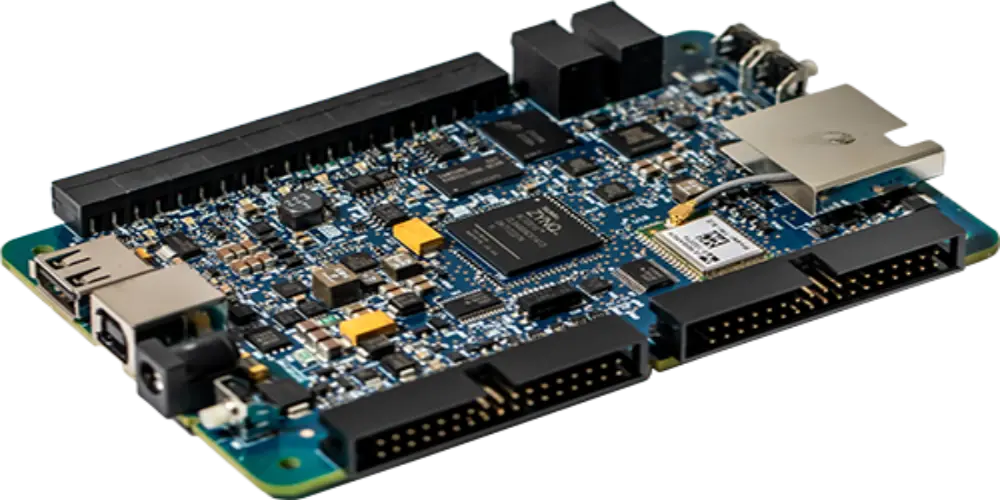
PCBA refers to a bare circuit board on which various electronic components are installed to form a complete circuit with specific functions. It can also refer to the process of assembling electronic components onto circuit boards.
What Are the Main Parts of PCBA?
PCB: The bare PCB board we talked above provides a platform for component installation.
Components: Various electronic components are required to perform specific functions, which may include resistors, capacitors, connectors, etc.
Solder Paste: Solder paste that attaches components to circuit boards.
Enclosure: The enclosure or box that houses the PCBA.
3 Common PCB Assembly Methods
Surface-Mount Technology(SMT)
Soldering components to the surface of circuit boards is known as the SMT assembly method. This is a highly automated technology that can make PCBs more compact, achieve miniaturization, and enhance electrical performance. Multi-layer PCBs often use this technology to mount components.
Through-Hole Technology (THT)
THT is a method of inserting electronic components with leads into holes on a PCB and fixing them with soldering. This approach results in a more robust connection between components and circuit boards, making the components more reliable and durable. Generally speaking, these components are larger than surface-mount components. Thru-hole technology is suitable for higher power and larger electronic components.
Mixed Technology
This is a hybrid technology that combines the advantages of both assembly methods to meet the requirements of different types of electronic component installation. SMT is used to install small-sized, high-density surface mount components. THT is used to install some larger, higher-power electronic components.
What Is the Relationship Between PCB and PCBA?

A printed circuit board is the foundation of printed circuit board assembly, providing a physical platform and electrical connections for the installation of electronic components. PCBA needs to install components on the circuit board to play a specific function, which means that PCB manufacturing is the first step in the PCBA manufacturing process.
PCB and PCBA affect each other. The quality and performance of the board will directly affect the final PCBA. Poor welding and component damage during the PCB assembly process will also cause circuit failures on the PCB.
PCB vs. PCBA: The Crucial Differences
In the previous content, we have introduced PCB and PCBA in detail. Next, we will compare them in several aspects to better comprehend and differentiate between PCB and PCBA.
| PCB | PCBA | |
| Composition | Blank board without any components. | A board with required components. |
| Functionality | Provides a physical platform and electrical connections. | A completed circuit board performing required functions. |
| Complexity | Determined by PCB layout and number of layers. | Determined by PCB, component quantity, type, arrangement, etc. |
| Cost | Low cost, only including PCB board cost. | Higher costs, including the cost of circuit boards, components, assembly fees, etc. |
| Assembly Techniques | Unnecessary. | SMT, THT, or mixed technology. |
| Repairability | Without installing components, only involves circuit board repairing. | Involving board repairing, component replacement, re-soldering, etc. |
We can see intuitively that PCB is just a blank board, while PCB is installed with complete components. This means that PCB has relatively few functions. However, PCBA can be directly applied to electronic devices and can perform specific functions such as signal adjustment and power control.
In terms of complexity, the complexity of the PCB depends on its layout design and the number of layers. A Reasonable layout and appropriate number of layers are determined by the performance of the PCB. In comparison, PCBA is more complex, because it not only needs to consider the factors of PCB, but also other factors. Numerous electronic components may affect each other, such as electromagnetic interference, signal crosstalk, etc. This increases the complexity and difficulty of PCBA manufacturing.
The cost of PCB is lower, which only includes the board manufacturing cost. The cost of PCBA is much higher, which includes the board cost, electronic component procurement cost, assembly cost, etc.
When it comes to repairability, PCB is relatively simple, involving only the circuit board itself. PCBA contains many electronic components, and this process involves replacing and re-soldering components. Different fault types and component layouts will also affect the complexity of repair.
Conclusion
Totally, PCB and PCBA play different roles in electronic manufacturing, but they are interrelated. Clearly distinguishing between PCB and PCBA, you can avoid misunderstandings when communicating with others. Consider your project’s requirements when choosing between PCB and PCBA.
At the stage of product design, a bare PCB is an ideal choice, it is more flexible and can make various adjustments and improvements. For some small batch products used for testing, choosing PCB will save more costs. It is mainly for product function testing and uncertain whether it will be mass-produced. When you need a circuit board that can perform a specific function directly in a device, PCBA is the best choice to save time. Especially in the mass production stage, the product quality requirements are high, and functional modules that can be used directly are required.