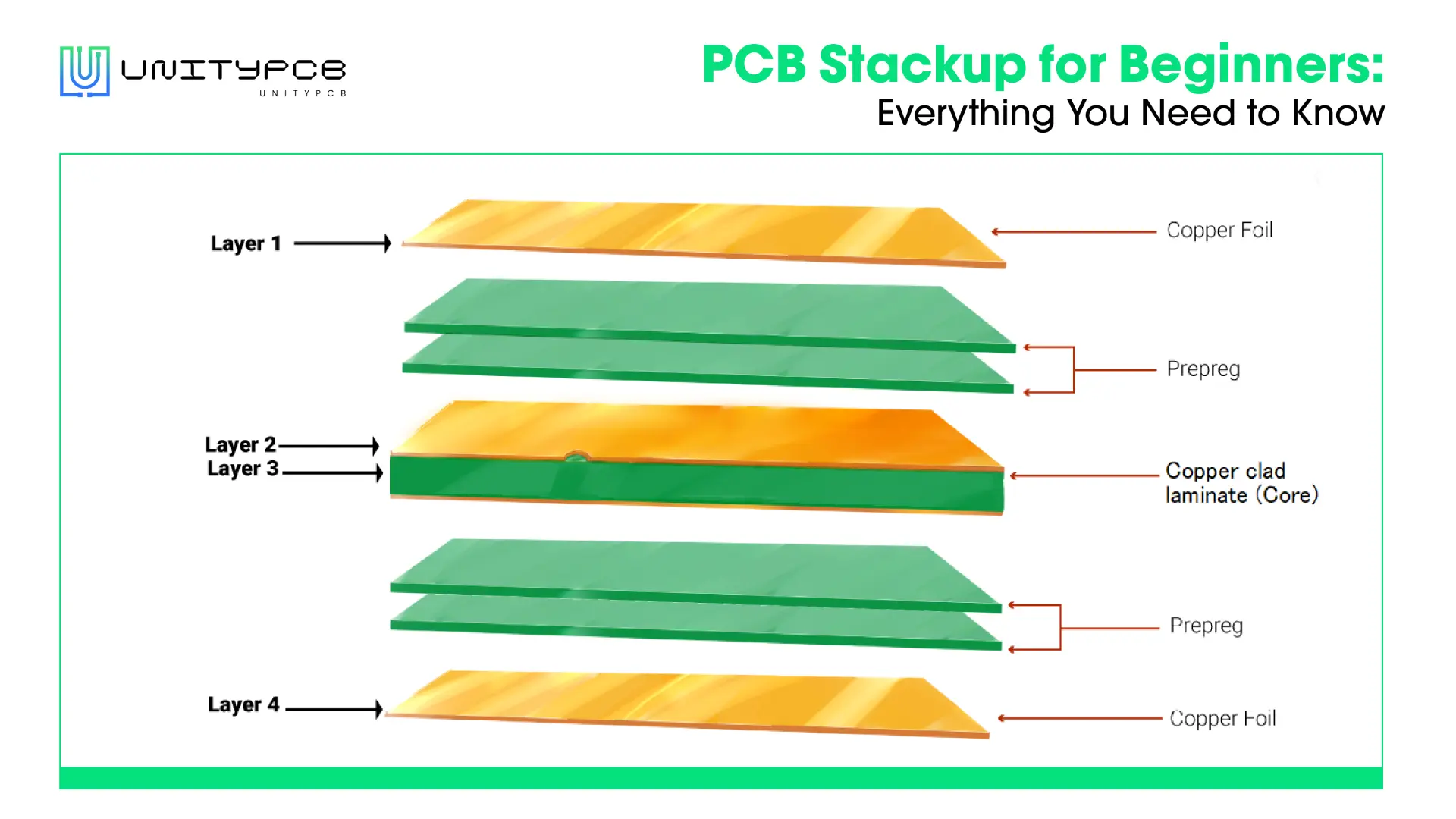
When manufacturing PCBs, you need to choose the right substrate for your final product. There are many choices for substrate materials, like metal, Rogers, FR4, etc. FR4 is one of the most commonly used materials. In this blog, we will introduce FR4 material characteristics in detail to help you understand the advantages and limitations of FR4 PCB.
What Is FR4?
FR stands for “fire retardant” and “4” means that the material is made of glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin. Technically speaking, FR 4 is not actually a type of material but a grade of material. The materials must meet the UL 94 V-0 flame retardant standard, which means that they can effectively suppress the spread of fire when the component overheats.
FR4 Material Characteristics
- Flame-retardant
As we have mentioned above, UL 94 V-0 has a higher flame rating which indicates the material has excellent fire resistance in vertical burn tests. V-0 indicates that once the fire source is eliminated, the material will quickly extinguish. FR4 material is suitable for applications where fire safety is extremely important.
- Excellent Electrical Properties
The dielectric constant of FR4 materials varies from 3.8 to 4.8, contingent on the material structure and composition. This dielectric property helps reduce signal loss and minimize crosstalk between adjacent circuit paths. FR4’s low dissipation factor enables controlled impedance to ensure signal integrity.
- Low Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption refers to the degree to which a material absorbs water when immersed in water, usually expressed as a percentage of weight increase. Test data shows that the moisture absorption of FR4 material after immersion in water for 24 hours is only 0.10%. This extremely low water absorption rate enables FR4 PCB to maintain stable shape and performance in humid environments.
- Thermal Properties
FR4 has poor thermal conductivity, about 0.3 to 0.4 W/m·K, which is much lower than metal. Its glass transition temperature (Tg) is between 130°C and 180°C. When it approaches this temperature, the performance will degrade, affecting the stability of the circuit board.
Variants of FR4
- Standard FR4
This material has a heat resistance of 130°C while combining good electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength. Standard FR4 is not suitable for extreme environmental conditions, and its comprehensive performance is sufficient to meet the application requirements of most circuit boards.
- High TG FR4
It is a high-temperature resistant PCB substrate whose notable feature is a glass transition temperature (TG value) of approximately 180°C. This is nearly 50°C higher than the TG value of standard FR4 materials. This material is more stable at high temperatures, and widely used in electronic equipment under high-temperature operating conditions.
- High CTI FR4
CTI (Comparative Tracking Index) measures the resistance of a material to the propagation of current along the surface of a material in a high humidity environment, that is, anti-tracking performance. High CTI FR4 material has better electrical insulation properties and can effectively prevent electrical failures in humid, polluted, or high voltage environments.
- Halogen Free FR4
Halogen-free FR4 is an environmentally friendly PCB substrate that is characterized by the absence of halogen compounds such as bromine. Halogen elements are often used to enhance certain properties, but they release toxic gases at high temperatures or during combustion, which are harmful to the environment and human health.
- FR4 with No Copper Laminate
Copper-free FR4 does not contain any copper layer or conductive traces. It retains the core advantages of FR4 material, like excellent mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and heat resistance. Due to these advantages, it is an ideal choice for structural support, brackets, and test boards.
What Role Does FR4 Play in PCB Manufacturing?
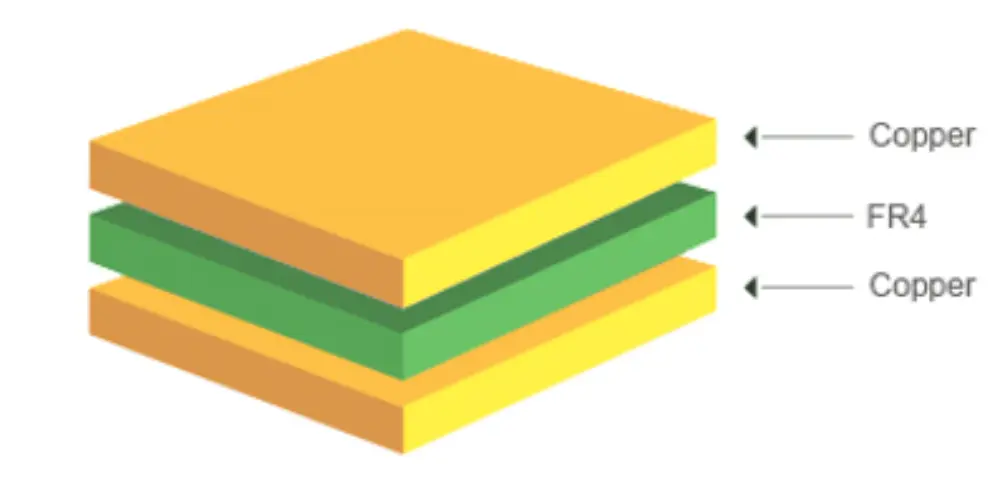
FR4 is a grade of glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin laminate, commonly used as the substrate material in FR4 PCB manufacturing. This substrate provides excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and heat resistance. With these properties, FR4 PCB is widely used in a number of electronic products from consumer electronics to industrial machinery.
Factors to Consider When Determining FR4 PCB Thickness
The thickness of FR4 PCB is typically 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm. This should be customized to the needs of its specific design. We will run through some of the factors you must consider when determining the FR4 PCB thickness.
Space Consideration: If there are restrictions in device space, the designers usually choose a thinner FR4 PCB. This often happens in small electronic devices like USB connectors and Bluetooth accessories. Even in bigger devices, the usage of thinner FR4 PCB can save internal space effectively.
Connector Matching: If a connector is needed, mismatching it with the thickness of the FR4 PCB could lead to slippage, instability, or even damage to the board. The matching compatibility of the connector should be matched during the design stage.
Impedance Matching: The thickness of FR4 PCB defines the thickness of the dielectric between every layer. This dielectric thickness is one of the big variables that affect impedance. For high-frequency circuit design, adjusting the thickness is an effective way to achieve impedance matching. This helps to maintain signal integrity and ensure stable performance.
Component Compatibility: When using through-hole components, FR4 PCB thickness needs to match the component pin length. Too thick a board may result in the component pins not being able to fully penetrate, affecting the normal function of the circuit.
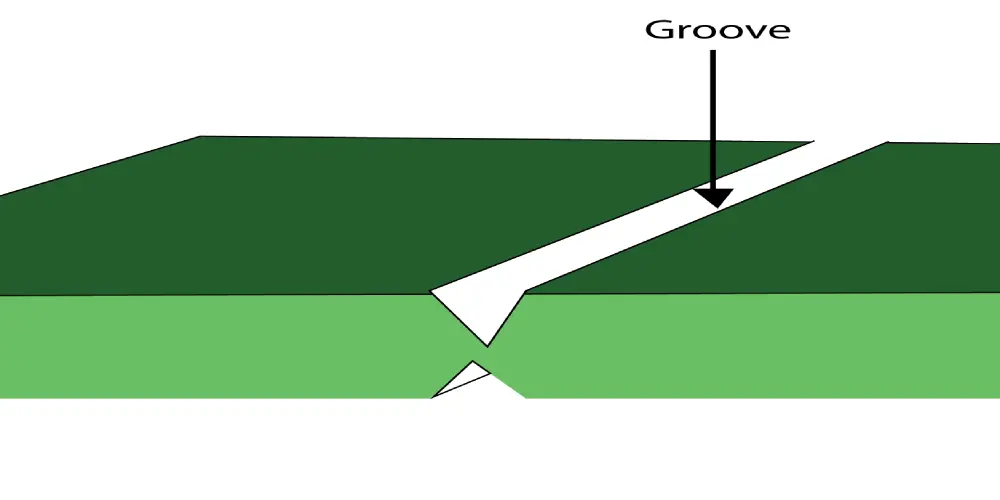
Design Requirements: Thin boards help save space, but they bring some limitations in design as well. It is not suitable for making large-size FR4 PCB, increasing the risk of fracture. A thin board is also not suitable for a PCB with V-grooves.
The Key Benefits of FR4 PCB
Cost Advantages
FR4 materials have cost advantages in PCB manufacturing, and the cost is much lower than other substrate materials, like metal. FR4 material is relatively inexpensive while providing good performance, making it an economical and practical choice for simple to complex multi-layer circuit board designs.
Excellent Mechanical and Electrical Properties
As an excellent electrical insulator, FR4 has good electrical properties. Its excellent mechanical strength also enables it to carry heavy electronic components and maintain stability in harsh environments.
Moisture Resistance
FR4 material offers excellent moisture resistance, with a water absorption rate near zero. This low water absorption capacity enables it to function steadily in humid environments. As such, FR4 is well-suited for use in humid environments or marine equipment.
Chemical Resistance
FR4 material has excellent chemical resistance, which is one of its important advantages as a circuit board substrate. It can withstand corrosion from various chemicals and solvents. This chemical resistance maintains the stability of material properties and enhances durability in harsh environments.
When FR4 PCB Boards Are Not the Ideal Choice
Given the many benefits of FR4 PCB, you might be wondering when it is not recommended to use it. Here, we list several FR4 circuit board constraints.
Too Thin for FR4
Due to the physical properties and thickness limitations of FR4 material, FR4 PCB is not suitable for very thin or small designs. For circuit boards that need to be thin and flexible, flexible PCBs are a better choice.
FR4 Resistance Limits
FR4 PCB has limited chemical resistance, and when exposed to corrosive chemical environments for a long time. The substrate will gradually degrade and fail. Secondly, the temperature resistance is limited, especially when lead-free soldering (up to 250℃) or high-temperature working environments are required. FR4 materials may be damaged due to their inability to withstand extreme temperatures.
Performance Limits of FR4
For FR4 PCB materials, the dielectric constant (Dk) is unstable. Compared with high-speed board materials, the dielectric constant of FR4 fluctuates greatly with frequency. Its tolerance can reach 10%, which is much higher than the 2% tolerance level of high-speed materials. This makes achieving stable controlled impedance on FR4 boards a challenge, especially in high-speed circuit designs.
Dissipation Factor Impact
FR4 substrates have a higher dissipation factor (Df) value of about 0.020. Compared to high-frequency laminates (Df of about 0.004), FR4 has a Df that is four times higher. This characteristic results in greater losses during signal transmission. As the frequency increases, the signal loss will be further exacerbated.
Get Your FR4 PCB Solutions from UnityPCB
UnityPCB is a world-renowned PCB manufacturing and prototyping expert with nearly 20 years of industry experience. We can provide customers with flexible low-volume production solutions and can meet a variety of PCB needs. As a professional FR4 PCB manufacturer, UnityPCB offers FR4 PCB manufacturing services with up to 18 layers, providing comprehensive solutions for your PCB problems. Contact us for a quote today.