Flexible PCB vs Rigid PCB are two common types of circuit boards, both widely used to connect electronic components. When choosing the right PCB for your project, it is essential to understand the key differences between these two types of PCBs. This blog will compare flexible PCB vs rigid PCB in depth to help you make an informed choice.
What Are Flexible PCBs and Rigid PCBs?
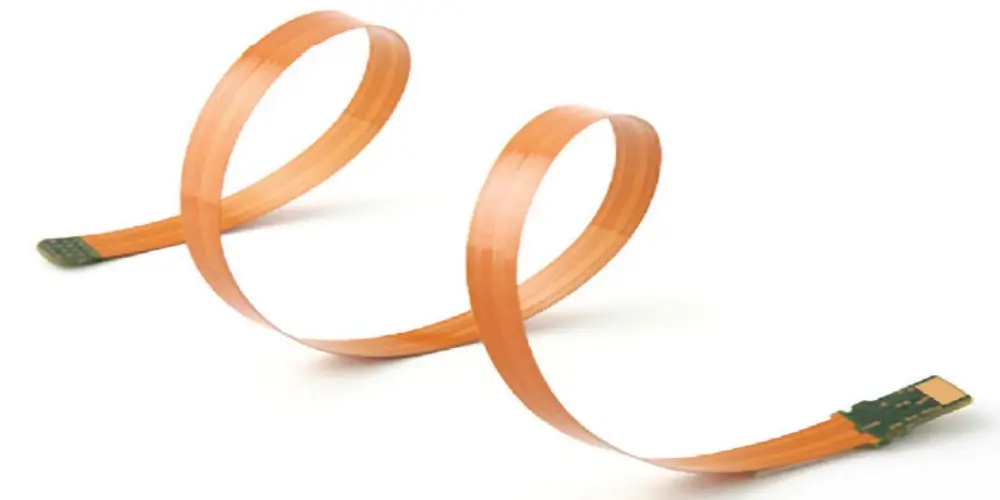

Flexible PCB
Flexible PCBs are usually made from flexible materials like polyimide, offering exceptional adaptability and versatility. Flex circuit boards can be bent and folded into various shapes. They are resistant to vibration and twisting. Their unique design allows them to fit into irregular spaces and confined environments, highly reducing the device’s space and weight.
Rigid PCB
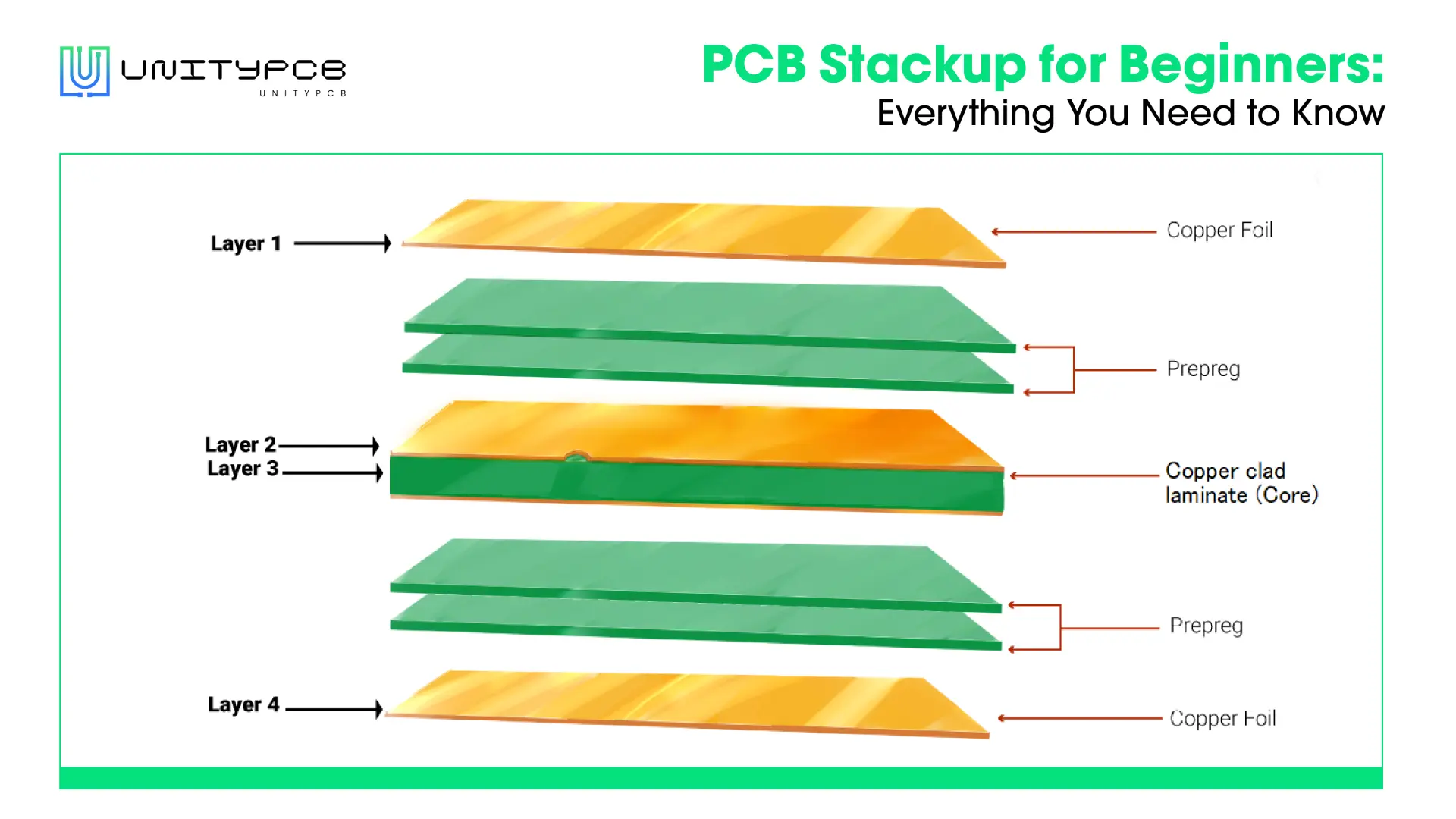
A rigid PCB, as the name suggests, is typically a non-flexible circuit board made from solid substrate material like FR-4. It features a stable structure that provides excellent mechanical support for the components assembled. Rigid circuit boards cannot bend or twist. Their shape is generally fixed and difficult to modify after manufacturing.
Key Factors to Consider When Designing Flexible and Rigid PCB
Flexible PCB
When designing a flexible PCB, it’s crucial to consider the following factors related to its flexibility characteristics.
- Bend Radius: The bend radius is the minimum radius that allows a flexible PCB can be safely bent without damaging the substrate material or breaking the conductive traces. Different flex circuit board material and thickness affect the bend radius. The bend radius you choose should be within the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure PCB functionality and reliability.
- Component Placement: Flexible PCB design requires special attention to component height, orientation, spacing, and layout.This helps avoid stress concentration caused by bending, which can lead to damage to solder joints or traces.
- Flexible to Rigid PCB Transitions: Flexible PCBs usually have a section that transitions from flexible to rigid.A smoother transition can be achieved by gradually reducing the thickness of the flexible area. The integrity of the PCB structure can be preserved with the use of stiffeners.
Rigid PCB
When designing a rigid PCB, consider the following key factors.
- Board Size Considerations: Rigid PCBs come in different sizes. Component size and layout, enclosure and device space constraints, etc., should all be considered when selecting the appropriate size.This ensures that the PCB fits the available space and is installed correctly.
- Mounting Method Selection: Rigid PCBs can use different mounting techniques, likeTHT (Through-Hole Technology) or SMT (Surface-Mount Technology). The selection of a mounting method needs to consider factors like component type, assembly process, and PCB mechanical strength. It is crucial to make sure that the selected mounting method is compatible with the overall design of the PCB.
- Stackup Design: Rigid PCBs are available in single-layer, double-layer, and multilayer designs, allowing for complex circuit designs.Layer stackup can impact PCB signal integrity, thermal management, and power distribution. During the design phase, the number of layers and layer arrangement should be carefully designed, and the ground layer and power layer should be reasonably configured.
Flexible PCB vs Rigid PCB: Key Differences Explained
In this table, we compare Flexible PCB vs Rigid PCB in 9 aspects, you can see their differences clearly.
| Aspect | Flexible PCB | Rigid PCB |
| Conductive Material | Bendable annealed copper | Inflexible electro-deposited copper or copper foil |
| Base Layer | Polyimide or polyester | FR-4 |
| Manufacturing process | Using an overlay process, using stiffener to provide mechanical support | Commonly uses a solder mask, often green |
| Cost Considerations | Generally more expensive due to flexible design complexity | More cost-effective and widely used |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, can bend and conform to shapes | Rigid and inflexible, cannot bend |
| Space Constraints | Ideal for space-constrained designs | Requires more space due to inflexibility |
| Weight | Light, thinner board | Heavier, thicker board |
| Durability and Resistance | Absorbs vibrations, resistant to shocks | More durable in stable, static environments |
| Design Complexity | More complex, especially for flexible part design | Less complex |
Choosing Between Flex and Rigid Circuit Boards
Through the above comparison, you should have a better understanding of flexible PCB vs rigid PCB. When to use flexible PCB vs rigid PCB hinges on multiple key factors.
Cost Considerations
Cost is the primary selection parameter when deciding whether to go for flexible PCB vs rigid PCB. Flex circuit boards’ production costs are typically higher than rigid circuit boards. The additional manufacturing and design costs of flex PCBs may offset their advantages. According to your project needs, you should find a balance between flexible PCB vs rigid PCB. When necessary, choose flexible circuit boards. Without compromising performance, it is recommended to give priority to rigid circuit boards. Rigid circuit boards are lower in cost and simpler to manufacture.
Space Constraints and Weight
Rigid PCBs are usually heavier than flexible PCBs due to their greater strength and thickness. They are suitable for applications with ample space. Flexible circuit boards are very suitable for small weight-sensitive devices or space-constrained applications because of their thin and bendable materials, which can effectively achieve lightweight design.
Reliability and Durability
Reliability is a critical factor in electronic devices, especially in applications where failure could have serious consequences. Both flexible PCB vs rigid PCB are reliable when properly designed and manufactured. Many factors can affect the reliability of PCBs, like operating conditions, environmental factors, design complexity, etc. For example, flexible PCB is typically made from polyimide, whose high-temperature resistance and flexibility allow it to perform well in extreme conditions. When choosing between flexible PCB vs rigid PCB, it’s critical to take into account the unique requirements of your application.
Where to Use Flex PCBs and Rigid PCBs?
Here we list some common applications of flexible PCB vs rigid PCB, showing how they are used in various industries.
Applications of Flex PCBs
Wearable Devices: Flexible PCBs have wide usage in wearable devices due to their foldable nature. Flex circuit boards can be integrated into devices like smart clothing, smart watches, and fitness trackers. They can adapt to the human body to provide higher comfort and functionality.
Aerospace: Flexible PCBs can withstand extreme temperature changes and severe impact pressure. It also has significant lightweight and space-saving properties, making it particularly suitable for satellites, aircraft avionics, and communication systems.
Medical: Flexible circuit boards bring unprecedented innovative possibilities to medical device design. From implantable devices to medical imaging systems and diagnostic equipment, the unique flexibility of flex PCB allows for more compact designs. Especially in medical wearable devices, flexible PCBS can flexibly adapt to the human morphology and provide excellent performance and durability for devices like hearing aids and heart sensors.
Automotive: Modern cars are increasingly dependent on electronic technology, integrating many sensors and electronic devices such as temperature control systems, GPS navigation, dashboard displays, rearview cameras, etc. Flexible PCBs can bend, fold, and adapt to complex shapes, making them suitable for use in scenarios such as cars where space is limited.
Applications of Rigid PCBs
Consumer Electronics: Rigid PCBs are widely used in consumer electronics that we use frequently, such as smartphones, tablets, and TVs. Due to their structural stability and easy component installation, rigid circuit boards are very suitable for large-scale production and can effectively control costs and ensure economic efficiency.
Aerospace: Aluminum-based rigid PCBs are popular for their excellent thermal conductivity in aerospace. It is widely used in various critical equipment.
Automotive: Rigid circuit boards have excellent mechanical properties and are resistant to vibration and harsh environments. Common applications include engine control units, infotainment systems, and safety modules.
Industrial Equipment: Rigid circuit boards are widely used in industrial equipment. This is because they can withstand harsh environmental conditions. You can find them used in control systems, motor drives, and power distribution units.
Final Thoughts
You should have a comprehensive consideration when choosing flexible PCB vs rigid PCB, as each type has its advantages and disadvantages. Rigid circuit boards are known for their stability and cost-effectiveness. Flexible circuit boards offer flexibility and compactness. It is crucial to understand the design considerations, differences, and practical applications of flexible PCB vs Rigid PCB. This will allow you to select a better and excellent choice for your project.