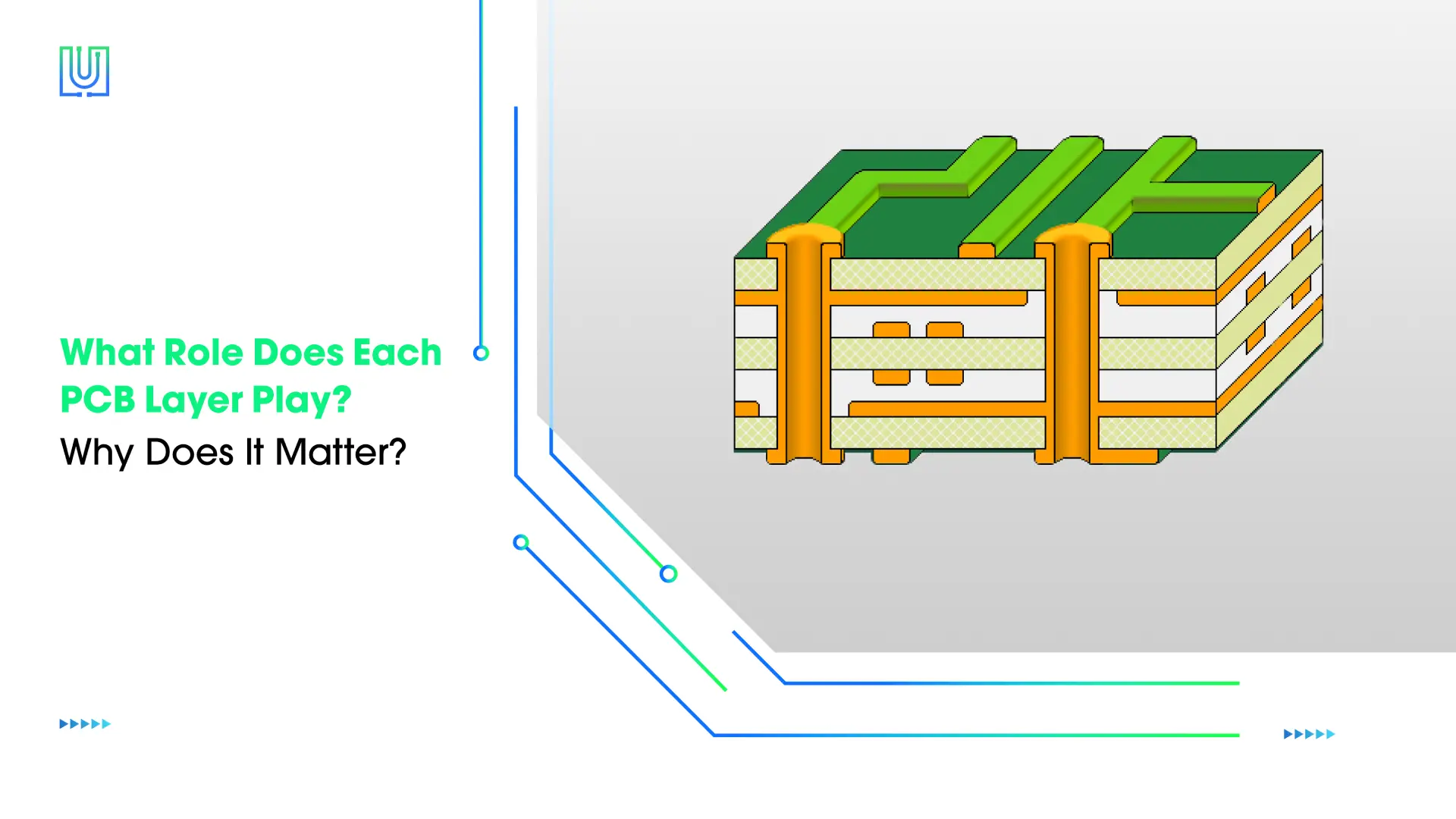
The core of contemporary electronic devices is printed circuit boards. You can find printed circuit boards in a variety of devices with different sizes, complexities, and functions. The products require different types of PCB to fulfill varying needs. How many types of PCB do you know? Usually, we classify the PCBs by layer, flexibility, material, and performance. This article will introduce types of PCB by these four classifications along with their advantages and applications.
Classification by Layer
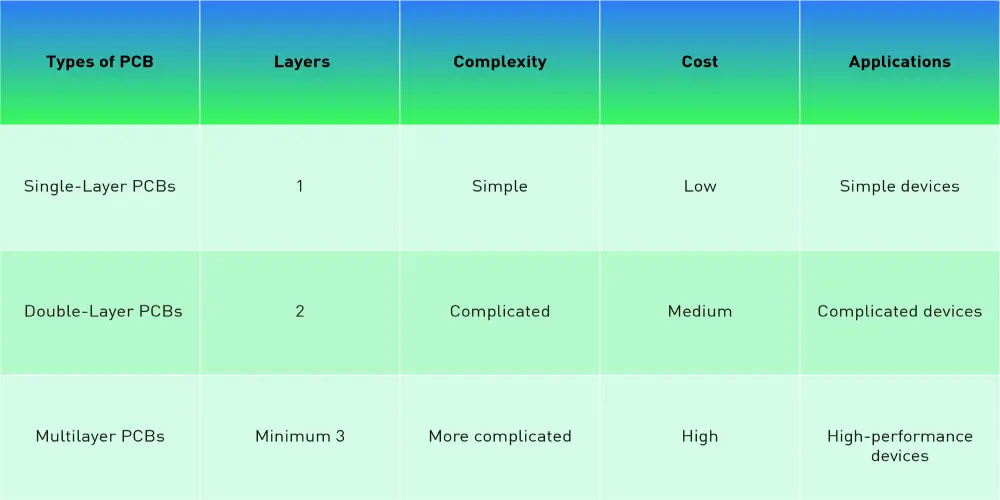
According to the number of layers, we introduce the following three types of PCB.
Single-Layer PCBs
Single-layer is the most simple and common type of PCB. There is only one conductive layer, usually copper, laminated on the substrate, and the electronic components are assembled on the other side. The top of the PCB is covered with the silk screen layer and solder mask.
This type of PCB only has one layer to conduct electronic signals, and the traces cannot cross or overlap. Thus, the circuit board needs to occupy a large space. It is popular for devices with a low density. A single-side PCB is easy to design and manufacture, so it is cost-effective and easy to mass produce. Meanwhile, when the circuit board has any problem during the running process, it is easy to find and repair it.
This type of PCB is popular for simple circuits, like toys, sensors, power suppliers, calculators, and so on.
Double-Layer PCBs
Compared with single-layer PCB, the double one has a conductive layer laminated on both sides of the substrate. The holes on the board can connect the circuit from two sides.
A double-layer PCB has more space to assemble the components on two sides, so it can reduce the space needed and increase the circuit density. That’s why it has more function, runs at a high speed with a low weight, and is more compact.
This type of PCB is more complex and suitable for advanced electronic devices, such as amplifiers, test devices, and LED lights.
Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs have at least three conductive layers, and insulating substrate layers are placed between each conductive layer. Then, different layers are laminated together with high temperature and pressure.
Multilayer circuit board has many layers from three up to 50 or more, it’s favored in advanced electronic devices with high performance, small space needed, flexible design, and stability.
Based on their excellent performance, these circuit boards are frequently employed in leading-edge medical devices, computers, cell phones, and other more complicated circuits and devices.
Classification by Flexibility
Below we will introduce three types of PCB in terms of flexibility.
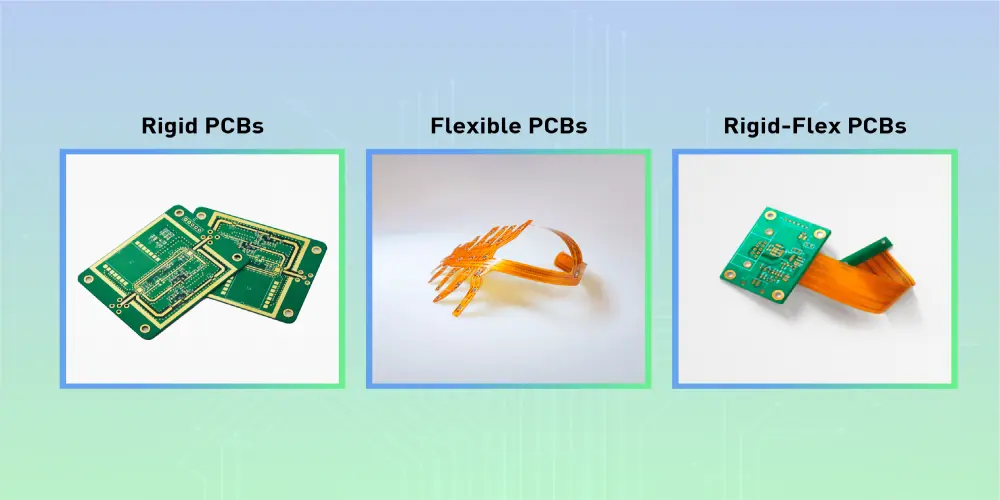
Rigid PCBs
We can learn from the name of the Rigid PCB, which is a board that cannot be bent and wrapped. This is because the basic substrate is a rigid material, which provides the board for hardness and strength.
Rigid PCBs can be single, double, or multilayer, according to actual needs. It is known for minimizing the electronic nose, resistance to movement, and ease of repair. Though the PCB is exposed to a bad application environment, the assembled components are hard to move.
Due to its advantages, rigid PCB boards are popular use in GPS devices, X-rays, temperature sensors, and so on.
Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs are used with flexible substrates, usually made of polyimide or polyester. This circuit board can wrap and bend into a variety of shapes thanks to these materials. Its outstanding flexibility makes it an ideal choice for those devices with flexible requirements and limited space, especially some wearable devices.
It is widely used in aerospace, consumer electronic devices, wearable devices, automotive devices, and medical devices.
Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the advantages of rigid and flexible circuit boards. This circuit board contains two types of PCB, a flexible circuit board connected to a rigid circuit board, and can be used in areas where both rigidity and flexibility are required. So circuit board containing two types PCB can be designed and created in 3D to adapt the special application while saving space.
Generally, these hybrid circuit boards are usually adopted in key applications of medicine and aerospace.
Classification by Material
Based on the different materials of the substrate, we introduce 4 types of PCB in detail.
FR-4 PCBs
FR is called flame retardant, and “4” refers to woven glass-reinforced epoxy resin. This material used as a substrate can provide FR-4 PCB for high-performance insulation, mechanical strength, heat, and chemical resistance. It’s the common substrate for a variety of PCBs.
Advantages:
Low cost: It is a relatively low-cost material.
Chemical resistance: It has excellent chemical resistance to many chemicals and can prevent substrate damage during circuit board assembly.
Mechanical strength: Avoid the substrate bend or wrap.
Flame retardant: Contains flame retardant materials to prevent fire from spreading.
Insulation: Have a good performance on resisting current flow.
Metal Core PCBs
Metal materials are typically used as substrates in most cases. In high-power circuits, insulating materials dissipate heat slowly and it is difficult to meet the heat dissipation requirements. Metals have the characteristics of high thermal conductivity. It typically used aluminum and copper as substrates.
With a metal substrate, the PCB can have good thermal management and improve the service life of components and the reliability of the entire circuit.
This type of PCB can be found in LED applications, power converters, and high-voltage regulators.
Advantages:
Longer lifetime: Aluminum is a very strong metal that has greater strength and durability than commonly used substrate materials. The risk of PCB board breakage can be reduced.
Thermal management: Metal has strong thermal conductivity.
Recyclable: Metals can be recycled. Aluminum is a recyclable metal that is not harmful.
Polyimide PCBs
Polyimide is a polymer that includes different natural and synthetic materials and it’s commonly used in flexible printed circuit boards. This material is more expensive than the commonly used FR-4 but is softer and has better heat and chemical resistance. This type of circuit board is popularly used in aerospace with high temperatures, medical with flexible requirements, and wearable devices.
Advantages:
Temperature resistance: Depending on the type of polyimide they are made of, polyimide materials can function in a variety of harsh environments and endure temperatures as high as 260℃.
Flexibility: Can be bent repeatedly without damage, ideal for applications requiring flexing
Chemical resistance: When exposed to acids or solvents, it does not dissolve or degrade easily, whereas FR-4 takes up moisture and breaks down more quickly.
Light weight: Compared with FR-4, it is lighter and can be used in portable and wearable devices.
Ceramic PCBs
Ceramic PCB is a board with ceramic as the substrate. It can quickly move heat away from hot spots and distribute it across the entire surface. They are used in various fields due to their high thermal conductivity and strong mechanical support.
Due to the special electrical properties of ceramic materials, it is especially suitable for radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications. This type of circuit board reduces signal loss while preserving signal integrity. We often find ceramic PCBs in the fields of telecommunications, aerospace, and satellite communications.
Advantages:
Thermal conductivity: Compared to traditional PCB, it can be used in high temperatures because of its high thermal conductivity, which enables it to endure high temperatures well without becoming damaged.
High-temperature tolerance: Can operate normally in a working environment up to 800 ℃.
Mechanical strength and durability: Relative to conventional PCBs, ceramic PCBs have greater mechanical strength and rigidity.
Signal integrity: Ceramic materials can preserve signal integrity at high frequencies because of their exceptional electrical qualities and low dielectric loss.
Classification by Performance
Classifying PCBs by performance, we will introduce two types of PCB for you.
High-Density Interconnect PCBs
When comparing a high-density interconnect PCB to a traditional PCB, the wiring density is higher. Higher connection pad density, smaller vias, and smaller spaces are also present.
For many applications requiring small size, high performance, and sophisticated functionality, HDI PCBs are indispensable. It is popularly used in smartphones, wearable devices, and medical devices.
Advantages:
Lighter and smaller size: More components can be mounted, resulting in a smaller and lighter circuit board
Excellent performance and reliability: The signal integrity of the HDI board is better, and cross-delay and signal loss are greatly decreased.
High-Frequency PCBs
High-frequency PCB is a circuit board with a frequency greater than 1GHz, which requires special materials to manufacture. This can meet special signal requirements in electronic equipment. It is widely used in advanced communication systems, military industry, and radar systems.
Advantages:
Low dielectric constant: A lower dielectric constant helps with frequency transmission and less signal delay. It allows for higher frequency transmission rates.
Low dissipation factor: The signal loss is small while the signal transmission is enhanced.
Final Thoughts
The above are the 12 common types of PCBs. Different types of PCBs possess distinct characteristics and are suitable for a range of applications. When we need to choose suitable PCBs, we commonly have to consider circuit complexity, design complexity, space limitations, cost, performance requirements, and so on. To select the most suitable PCB board, we must carefully comprehend several factors. Looking into the future, more types of PCB will appear to meet the higher requirements and performances of different devices in all kinds of industries.