Green PCBs have been the industry standard for years due to their cost-effectiveness, ease of manufacturing, and long history of use. However, in the last few years, blue PCBs have become more and more popular. We can find them in consumer gadgets, custom prototypes, and industrial equipment. But why are they so attractive? Blue circuit boards are not just pretty to look at, there are many benefits to using them. In this blog, we’ll discuss their advantages, their applications across various industries as well as how they are manufactured.
What Is a Blue PCB?
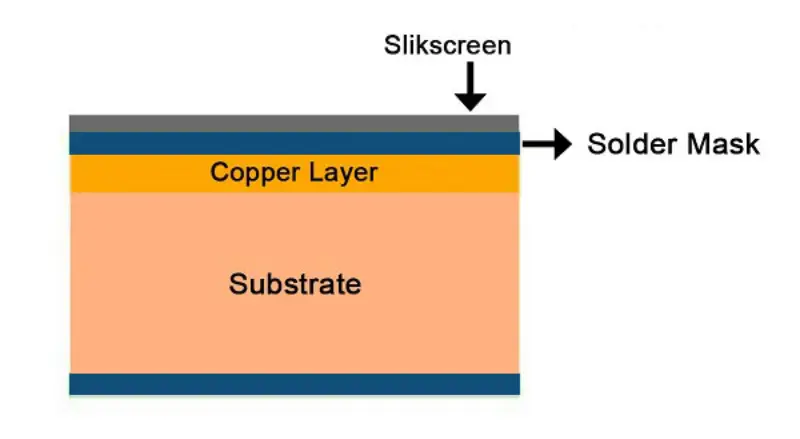
A blue PCB is a type of printed circuit board with a blue-colored solder mask. The solder mask is a layer of film applied to the copper traces on the PCB to protect against oxidation, prevent short circuits as well as improve the durability of the board. The color of the solder mask is not something done just for look, it has a functional value. And the blue color is influenced by type of epoxy resin used in the process.
The Composition of Blue Printed Circuit Board
The composition of a blue PCB is essentially similar to other standard PCBs, but with one key difference: the color of the solder mask. To understand the materials and processes involved in creating a blue PCB, let’s break it down:
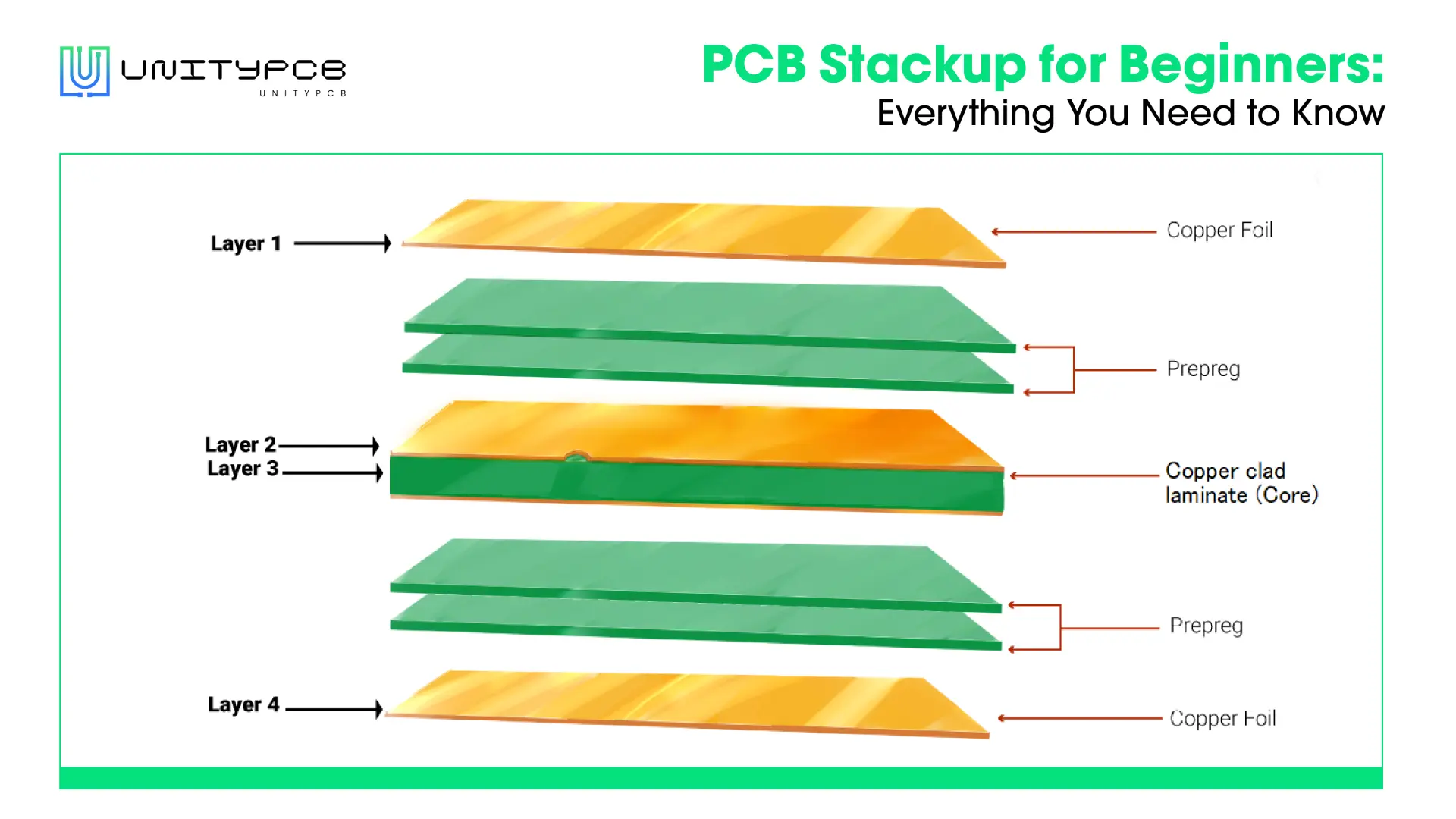
- Substrate Material: Typically,the core material used for the base of a PCB is fiberglass (FR4), ceramic, or polyimide. The substrate layer provides mechanical strength and foundation for the copper traces and solder mask.
- Copper Layer: The copper layer in a PCB is a conductive layer that is made from a think sheet of copper. It is etched away to form the circuit pathways that allow electrical signals to travel across the PCB.
- Solder Mask (Blue): The blue solder mask is a layer of epoxy resin masking over the copper tracesto protect them from moisture, dust and potential short circuits. It also helps to prevent oxidation of the copper traces, making the PCB last longer and reliably.
- Silkscreen Layer:Above the solder mask, a silkscreen layer is applied, normally in white, to print text and symbol such as components labels, polarity marks, and other notes. This layer makes critical information visible during assembly and maintenance.

How Are Blue PCBs Made?
The same basic process is used for blue PCBs as for other PCBs: design, etching, component placement and soldering. Though, the main distinction is the use of the blue solder mask.
- Design: Using CAD software,the designer specifies dimensions, layout, and electrical connections to create the PCB design. During this process, designers also need to choose the material and solder mask color.
- Etching: Next, etching copper foil on top of the substrate to form the conductive traces, which create electrical paths.
- Solder Mask Application: In this step, a layer of blue solder mask is applied over the etched copper to protect the circuit from the environmental factors and to improve the board mechanical strength. It also assists in a visual inspection of PCBs by offering the high contrast backdrop of the solder mask.
- Component Mounting: When the solder mask is cured,electronic components are then mounted on board either with SMT (Surface Mount Technology) or THT (Through Hole).
- Testing and Inspection: We put the Blue PCB through several quality control steps including Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)and X ray inspections to make sure there are no miss soldered connections and all components are assembled
Further Reading: How to Test PCB? 7 PCB Testing Methods You Should Know
Benefits of Blue Circuit Board
- Better Visibility for Inspection and Testing
With the blue solder mask providing high contrast against the copper traces, engineers and technicians will be able to inspect the board more easily during assembly and after soldering. Where visibility is critical to producing a good quality PCBA, this is especially important in complex boards with fine pitch components.
- Aesthetic Appeal
Compared to most circuit board designs, the visual profile of blue PCBs is distinctive. To differentiate their products, manufacturers of high end consumer electronics actively use blue solder masks. The blue coloration is professional looking and that it looks technological, especially in custom built electronic devices or on limited editions.
- Heat Dissipation
The PCB color can slightly affect thermal management characteristics. Compared to black and green PCBs, blue circuit boards have a reflective surface property, which can potentially improve heat dissipation. This becomes especially important in high-power electronic applications and applications where the thermal performance is important.
Applications of Blue PCBs
Blue PCBs have a large range of applications, especially in those industries in which aesthetics or prototyping play a key role.
Consumer Electronics: Blue PCBs are pervasive with many high-end consumer electronics such as smartphones, wearables and gaming devices. This fits well with the aesthetic demands of these products, a clean, modern look.
IoT Devices: Now with the Internet of Things (IoT) devices becoming more and more popular, blue PCBs are a popular choice for these kinds of products. IoT devices often need to stand out visually and may be used in environments where inspection is frequent. Quick visibility and easier maintenance is achieved with the blue PCB.
Custom and Prototype Projects: Blue PCBs are commonly used in prototypes, custom PCB designs, or one-off projects where design uniqueness is important. The ability to choose the color of the soldermask makes it easier to differentiate between different versions of a product or prototype during development.
Specialized Industries: In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, blue PCBs may be used in critical systems where functionality, reliability, and inspection ease are paramount. The unique color helps distinguish these boards from others and ensures a more professional look for advanced devices.
Blue PCB Vs. Green PCB: Which One is Better?

Green PCBs have dominated the market for decades due to their low cost, but blue PCBs are gaining ground with distinct advantages. The choice isn’t just about color – it’s about performance and design requirements.
Blue PCBs offer superior solder mask quality, providing better environmental protection and easier component inspection. Their higher-contrast surface makes trace and marking visibility significantly clearer. While slightly more expensive, they deliver improved heat dissipation and a more professional appearance.
For engineers, the decision comes down to specific project needs: budget constraints, performance requirements, and overall design vision. Neither color is universally superior; the right PCB depends on your unique application.
Recommended Reading: PCB Colors Explained: Selecting the Perfect Color for Your Circuit Board
Conclusion
With its aesthetic appeal, durability, and functional advantages, blue PCBs have extensive applications, including the production of consumer electronics, electronics, and automobiles and in industrial applications. If you are designing a new LED light fixture, a high end smartphone, or a medical device, it is clear that choosing blue PCBs is what you should be doing.
We, at UnityPCB, provide quality blue PCBs with your specified requirements. With our focus on quality, and our state of the art manufacturing capabilities, you will get a product that will exceed your expectations. To find out more about our blue PCB services, contact us today.