The printed circuit board serves as the backbone for the majority of the electronic gadgets we use in our increasingly digital environment. PCB surface finishes are a relatively easy process to overlook in the production of circuit boards, but they can affect the reliability, functionality, and service life of the final product. PCBs can be used with different types of PCB surface finishes. Given the wide range of surface finish options available, it’s critical to comprehend their distinct roles and limitations. This article will take you through 5 type of PCB surface finishes, detailing their distinct characteristics and differences and giving tips to choose your perfect one.
Why Do Circuit Boards Need a Surface Finish?
The PCB surface finishes of a circuit board is a coating on the copper surface of the exposed and solderable areas of the board. It is a protective coating and the life span of the printed circuit board can be increased. At the same time, it gives a flat finish for the electronic components to be soldered onto the board easily. It is crucial for successful PCB assembly.
The electrical performance and functionality of the board are related to the PCB surface finishes. Increased resistance, reduced electrical performance, and even failure, can be caused by copper oxidation. In addition, in certain harsh environments like high humidity, extremes of temperature, and chemical exposure, PCB surface finishes act as a protective layer to guarantee that the PCB runs properly through its lifetime. Copper oxidation can cause signal integrity problems, especially in some high-frequency and high-speed PCBs.
Top 5 PCB Surface Finishes Types You Should Know
We now understand the function and significance of PCB surface finishes, which enhance the PCB’s general dependability and durability. Then, we will detail 5 top PCB surface finishes and explain their characteristics.
1. Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL)
HASL is one of the most popular and conventional finish types. The process is dipping a blank circuit board into molten solder which will cover the copper. Excess solder is then removed using a hot air knife, and the board surface is leveled. The surface is not perfectly flat and is therefore not suitable for small components that use surface mounting technology. Solder is normally a tin and lead alloy in the ratio of 63% tin and 37% lead.
Most HASL lines are designed vertically so that the PCB can be fully immersed in the solder bath. Horizontal lines are also available, the solder distribution will not be affected by gravity and the thickness will be more uniform.
Advantages of HASL: Affordable, Used for mass production, Easily reworked, Fits through-hole components
Disadvantages of HASL: Includes lead (Does not meet RoHS standards), Uneven soldering surface, Not suitable for small electronic components
Lead-free HASL
HASL contains lead, a toxic substance that is bad for both people and the environment. RoHS has strict restrictions on electronic products containing lead, which has further contributed to the widespread use of lead-free HASL techniques. These two technologies are the same, the only difference is that lead-free HASL solder doesn’t contain lead.
2. Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG)
ENIG is a two-layer metal finish. The first layer is electroless nickel plating on copper and the second layer is immersion gold to protect the nickel during storage and extend the shelf life.
Coating thickness affects the PCB performance and dependability. The gold layer thickness can impact solderability and lead bonding. The nickel layer thickness plays an important role in preventing diffusion of the gold layer into the copper.
Nickel resists oxidation well at high temperatures, and therefore a good electrical connection between the component and the printed circuit board is maintained during the high-temperature soldering.
What Is Black Pad in ENIG?
Black pads are a flaw in the ENIG surface finishes that result from the nickel layer corroding too much during the gold plating procedure. Corroded nickel surfaces can prevent the formation of solder joints, which can result in problems of solder joint failure, a critical issue for PCB reliability.
These PCB surface finishes cannot be reworked, so we prefer to avoid these problems. Precisely controlling the temperature, pH, and chemistry of the nickel bath can thereby maintain the stability of the nickel layer and reduce the risk of corrosion.
Advantages of ENIG: Excellent corrosion resistance, Suitable for fine-pitch SMT components, Outstanding electrical conductivity, High thermal efficiency, Exceptional solderability
Disadvantages of ENIG: High cost, Possibility of black pad defects, Restricted reworkability
ENEPIG Finishes
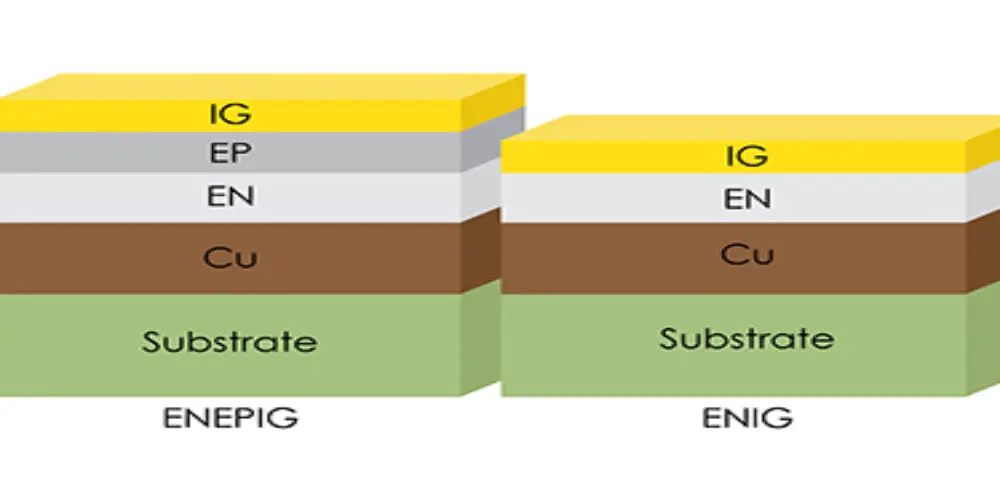
ENEPIG is a palladium plating added between the nickel and gold layers to separate them and prevent contact. This effectively solves the oxidation of the nickel layer and avoids the appearance of the defect of black pads.
3. Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP )
OSP is an organic surface finish in which organic materials react with the exposed copper surface to form a protective layer to prevent copper oxidation. During the ensuing soldering process, the organic protective film can be quickly removed by the flux, and then the copper and melted solder can form a solid solder joint in a short period of time. Boards coated with OSP have good wettability and are more advantageous in terms of solder wetting and melting, with the metal in the solder bonding more easily to the PCB or electronic assembly. Because of its affordability and environmental friendliness, it has become more and more popular.
Advantages of OSP: Low-cost, Good solderability, Environment-friendly, High wetting capability, Easy to produce, Easy to rework
Disadvantages of OSP: Unsuitable for PTH PCB, Easily damaged (Thin protective film), Unfit for harsh environmental conditions
4. Immersion Tin
Immersion tin is the chemical plating process where tin is deposited on the exposed copper of a circuit board. We typically see a white tin layer as protection for the copper. The surface is flat and smooth and is ideal for fine-pitch surface mount components. But the two metals have a strong affinity for each other and snuggling into each other. This can result in tin lines which can short circuits, negatively affect solder joints, and degrade the performance of the PCB.
Advantages of Immersion Tin: Cost-effective, Good solderability, Ideal for fine-pitch components
Disadvantages of Immersion Tin: Tin whisker, Hard to rework, Easily damaged immersion coating
5. Immersion Silver
The process of depositing a layer of silver on the bare copper surface is a silver immersion process where copper and silver are interchanged in a spontaneous reaction. Within the silver impregnation, some organic substances are used to avoid silver dissolution and reduction. Silver immersion coating for good electrical properties and good solderability in high temperature and humid environments. The electrical conductivity of immersion silver is better than that of OSP. Compared to ENIG, silver has lower strength than gold when used as a contact surface.
Advantages of Immersion Silver: Flatness excellent, Suitable for small components, Re-workable
Disadvantages of Immersion Silver: Need storage carefully, Sensitive to chlorine and sulfur compounds
A Comparison of 5 Surface Finishes
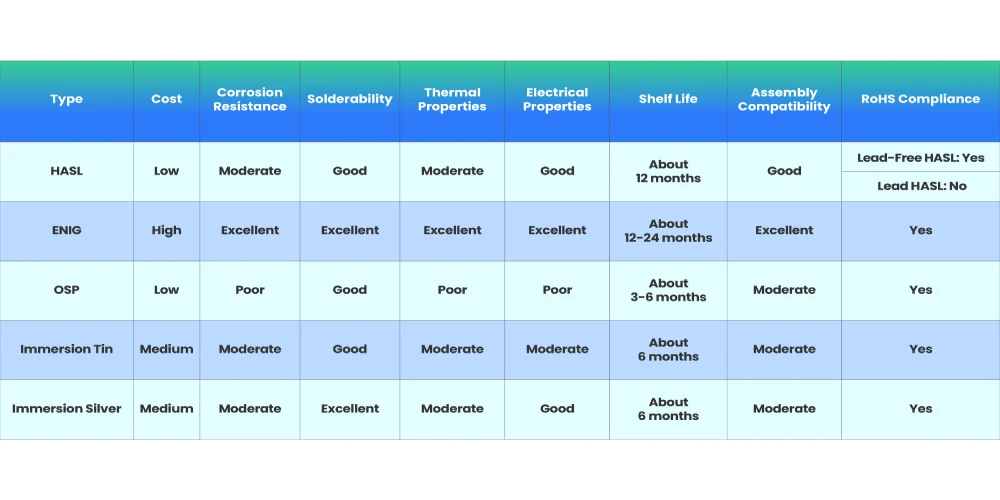
Through the above comparison table, we know that it is necessary to consider many factors when choosing PCB surface finishes. These include product performance requirements, budget, regulations, and assembly technology.
In most aspects, ENIG performs very well, but the cost is relatively high. When cost is not the primary limitation and the product performance requirements are extremely high, it is likely to be the first choice. OSP has been shown as an economical solution but should be considered in terms of limitations on thermal performance, electrical performance, and shelf life. Furthermore, the storage environment and packaging method will also affect the real shelf life of the end product.
How to Select the Perfect Surface Finish?
Below we will offer some advice on finish selection after an overview and comparison of the five PCB surface finishes mentioned above.
Cost Considerations
Choosing a surface finish requires a combination of many factors. It has to suit the budget of the whole project. However, if you have a higher budget, ENIG may be a good choice, and it will increase PCB’s reliability and performance. If the budget is limited, another option may be an alternative without compromising performance requirements.
Durability and Reliability
It protects the copper from oxidation and acts as a flat surface for components to be more easily assembled. For the expected performance and lifetime of the PCB, we need to choose suitable PCB surface finishes to guarantee the PCB’s function. Of course, ENIG is more durable and reliable.
Environmental Factors
Another important component in determining PCB performance is the working environment. We have to now take into account factors including temperature, humidity, and if there is chemical exposure. In harsh environments, PCB surface finishes must consider the actual performance requirements and environmental influences when selecting finishes to enhance reliability and durability.
Compliance Requirements
There are three regulations concerning the quality and safety of electronic products: RoHS, REACH, and IPC Standards. Manufacturers must make sure their items comply with these rules. RoHS severely restricts the use of hazardous materials, such as lead. Therefore, you need to take care that HASL is not compliant with this standard.
Last Thoughts
Choosing PCB surface finishes correctly is one of the most critical decisions when choosing for your PCB. However, once you compare the five surface finish types, you will better understand which surface finish you will pick so as to improve product reliability and comply with the project requirements. The further development of technology will make PCB surface finishes play an increasingly important role so that the electronic products in our lives will be developed into reliable, efficient, and high-quality electronic products.